New avenues of exploration for erythropoietin
- PMID: 15632341
- PMCID: PMC2254180
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.293.1.90
New avenues of exploration for erythropoietin
Abstract
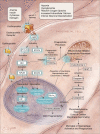
Discovery that the hormone erythropoietin (EPO) and its receptor play a significant biological role in tissues outside of the hematopoietic system has fueled significant interest in EPO as a novel cytoprotective agent in both neuronal and vascular systems. Erythropoietin is now considered to have applicability in a variety of disorders that include cerebral ischemia, myocardial infarction, and chronic congestive heart failure. Erythropoietin modulates a broad array of cellular processes that include progenitor stem cell development, cellular integrity, and angiogenesis. As a result, cellular protection by EPO is robust and EPO inhibits the apoptotic mechanisms of injury, including the preservation of cellular membrane asymmetry to prevent inflammation. As the investigation into clinical applications for EPO that maximize efficacy and minimize toxicity progresses, a deeper appreciation for the novel roles that EPO plays in the brain and heart and throughout the entire body should be acquired.
Figures
Comment in
-
Erythropoietin and cancer.JAMA. 2005 Apr 20;293(15):1858; author reply 1858-9. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.15.1858-a. JAMA. 2005. PMID: 15840858 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Erythropoietin in the brain: can the promise to protect be fulfilled?Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004 Nov;25(11):577-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2004.09.006. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15491780 Review.
-
Apaf-1, Bcl-xL, cytochrome c, and caspase-9 form the critical elements for cerebral vascular protection by erythropoietin.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003 Mar;23(3):320-30. doi: 10.1097/01.WCB.0000050061.57184.AE. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003. PMID: 12621307
-
Do non-hemopoietic effects of erythropoietin play a beneficial role in heart failure?Heart Fail Rev. 2008 Dec;13(4):415-23. doi: 10.1007/s10741-008-9084-z. Epub 2008 Jan 31. Heart Fail Rev. 2008. PMID: 18236153 Review.
-
Erythropoietin and the heart: physiological effects and the therapeutic perspective.Int J Cardiol. 2014 Feb 1;171(2):116-25. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.12.011. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24377712 Review.
-
Erythropoietin and the vascular wall: the controversy continues.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013 Dec;23 Suppl 1:S37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2012.04.002. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2013. PMID: 22682530 Review.
Cited by
-
Transplantation of genetically engineered cardiac fibroblasts producing recombinant human erythropoietin to repair the infarcted myocardium.Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2008 Nov 3;1(1):7. doi: 10.1186/1755-1536-1-7. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2008. PMID: 19014419 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic cytokines for cardiac repair: mobilization of bone marrow cells and beyond.Basic Res Cardiol. 2011 Sep;106(5):709-33. doi: 10.1007/s00395-011-0183-y. Epub 2011 May 4. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21541807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinamide: Oversight of Metabolic Dysfunction Through SIRT1, mTOR, and Clock Genes.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2020;17(5):765-783. doi: 10.2174/1567202617999201111195232. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 33183203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Life versus cell longevity: the mysteries surrounding the NAD+ precursor nicotinamide.Curr Med Chem. 2006;13(8):883-95. doi: 10.2174/092986706776361058. Curr Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 16611073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Principles of antegrade cerebral perfusion during arch reconstruction in newborns/infants.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg Pediatr Card Surg Annu. 2008:61-8. doi: 10.1053/j.pcsu.2007.12.005. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg Pediatr Card Surg Annu. 2008. PMID: 18396227 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Uchida E, Morimoto K, Kawasaki N, Izaki Y, Abdu Said A, Hayakawa T. Effect of active oxygen radicals on protein and carbohydrate moieties of recombinant human erythropoietin. Free Radic Res. 1997;27:311–323. - PubMed
-
- Chong ZZ, Kang JQ, Maiese K. Hematopoietic factor erythropoietin fosters neuroprotection through novel signal transduction cascades. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22:503–514. - PubMed
-
- Chong ZZ, Kang JQ, Maiese K. Angiogenesis and plasticity: role of erythropoietin in vascular systems. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2002;11:863–871. - PubMed
-
- Genc S, Koroglu TF, Genc K. Erythropoietin as a novel neuroprotectant. Res Neurol Neurosci. 2004;22:105–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

