Cytotoxicity of epigallocatechin-3-gallate to LNCaP cells in the presence of Cu2+
- PMID: 15633248
- PMCID: PMC1389627
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.2005.B0125
Cytotoxicity of epigallocatechin-3-gallate to LNCaP cells in the presence of Cu2+
Abstract
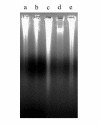
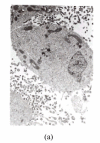
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) has shown remarkably anti-cancer activity, with its bioactivity being related to reactive conditions, such as pH and metal ions. The present study investigated the degradation of EGCG and its effect on prostate cancer cell in the presence of Cu2+. EGCG was incubated with prostate cancer cells, LNCaP, pretreated with or without Cu2+. EGCG in F-12 medium was quantified using HPLC and the viability of cells was assessed by gel electrophoresis, flow cytometry, and electron microscope. The results of HPLC showed that EGCG degraded completely within 12 h in F-12 medium with or without Cu2+. Gel electrophoresis and flow cytometry did not detect apoptosis of LNCaP cells when they were incubated with EGCG. Electron microscopy examination revealed that EGCG-Cu2+ complex led to damage of cytoplasm membrane in LNCaP cells. It was speculated that not EGCG, but its oxide and complex with Cu2+, are the bioactive components responsible for its cytotoxicity to LNCaP prostate cancer cells.
Figures











References
-
- Chung LY, Cheung TC, Kong SK, Fung KP, Choy YM, Chan ZY, Kwok TT. Induction of apoptosis by green tea catechins in human prostate cancer DU145 cells. Life Sciences. 2001;68(10):1207–1214. - PubMed
-
- Chung JY, Park JO, Phyu H, Dong ZG, Yang CS. Mechanisms of inhibition of the Ras-MAP kinase signaling pathway in 30.7b Ras 12 cells by tea polyphenols (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and theaflavin-3,3′-digallate. The FASEB Journal. 2001;15:2022–2024. - PubMed
-
- Cutter H, Wu LY, Kim CD, Morre J, Morre DM. Is the cancer protective effect correlated with growth inhibitions by green tea (-)-epigallocatechin gallate mediated through an antioxidant mechanism? Cancer Lett. 2001;162(2):149–154. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Ahmad N, Nieminent AL, Mukhtar H. Growth inhibition, cell-cycle dysregulation, and induction of apoptosis by green tea constituent (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in androgen-sensitive and androgen-insensitive human prostate carcinoma cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 2000;164(1):82–90. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Hussain T, Mukhtar H. Molecular pathway for (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human prostate carcinoma cells. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2003;410(1):177–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

