Transfection and expression of exogenous gene in laying hens oviduct in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 15633250
- PMCID: PMC1389629
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.2005.B0137
Transfection and expression of exogenous gene in laying hens oviduct in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
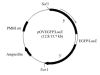
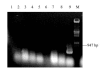
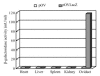
To examine whether or not the regulatory sequence of chicken ovalbumin gene can drive transgene expression specifically in hen oviduct, the authors constructed an oviduct-specific expression vector (pOV), containing 3.0 kilobases (kb) of the 5'-flanking sequence and 3.0 kb of the 3'-flanking sequence of the chicken ovalbumin gene. Jellyfish green fluorescence protein (EGFP) reporter gene and bacterial LacZ reporter gene were respectively inserted into the downstream of the 5'-regulatory region. The recombinants were named as pOVEGFP and pOVLacZ. Two transfer systems, in vitro and in vivo, were used to verify the function of the vector. In vitro, the plasmid DNA pOVEGFP and pEGFP-N1 were transfected respectively by the polyethyleneimine procedure into the primary chicken oviduct epithelium (PCOE) and fibroblasts cells isolated from laying hens. In vivo, the recombinant vector pOVLacZ was injected into egg-laying hens via wing vein and the tissues were collected for RT-PCR analysis. The results showed that expression of pEGFP-N1 was achieved at low level in oviduct epithelial cells and at high level in fibroblasts, but that the recombinant vector was not expressed in both cells. RT-PCR analysis showed that the LacZ gene was transcribed in the oviduct, but not in the heart, liver, kidney and spleen of the injected hens. Accordingly, the beta-galactosidase activity was only detected in the oviduct magnum (116.7 mU/ml) and eggs (16.47 mU/ml). These results indicated that the cloned regulation regions of chicken ovalbumin gene could drive exogenous gene expression specifically in the oviducts of hens. In vivo gene injection via wing vein may serve as a rapid production system of recombinant proteins in chicken eggs. In addition, the cultured primary oviduct cells from laying hens were not efficient temporary expression systems for analyzing the function of regulating elements of ovalbumin gene.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Generation of transgenic chicks using an oviduct-specific expression system.Genet Mol Res. 2011 Dec 8;10(4):3046-55. doi: 10.4238/2011.December.8.1. Genet Mol Res. 2011. PMID: 22180038
-
[GFP reporter gene under the direction of chicken ovalbumin gene promoter expressed in the CHO cell and in the primary cell cultures of chicken oviduct].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2005 Jan;21(1):154-8. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2005. PMID: 15859347 Chinese.
-
Modulation of transcriptional activity of the chicken ovalbumin gene promoter in primary cultures of chicken oviduct cells: effects of putative regulatory elements in the 5'-flanking region.Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1995 Jul;36(4):811-6. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1995. PMID: 8528143
-
Relationship between Mucosal Barrier Function of the Oviduct and Intestine in the Productivity of Laying Hens.J Poult Sci. 2022 Apr 25;59(2):105-113. doi: 10.2141/jpsa.0210090. J Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35528386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of prognostic factors for diagnosis and treatment of epithelial-derived ovarian cancer from laying hens.J Cancer Prev. 2013 Sep;18(3):209-20. doi: 10.15430/jcp.2013.18.3.209. J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 25337548 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adipogenic differentiation of chicken epithelial oviduct cells using only chicken serum.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011 Oct;47(9):609-14. doi: 10.1007/s11626-011-9452-1. Epub 2011 Sep 23. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2011. PMID: 21938588
-
Oviduct-specific expression of tissue plasminogen activator in laying hens.Genet Mol Biol. 2011 Apr;34(2):231-6. doi: 10.1590/s1415-47572011005000011. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Genet Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21734822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haecker SA, Muramatsu T, Sensenbaugh KR, Sanders MM. Repression of the ovalbumin gene involves multiple negative elements including a ubiquitous transcriptional silencer. Mol Endocrinol. 1995;9(9):1113–1126. - PubMed
-
- Hiroshi O, Hyi-Man P, Akihiro N, Ryuzo S, Jun-Ichi O, Tatsuo M. Synthesis of human erythropoietin in vivo in the oviduct of laying hens by localized in vivo gene transfer using electroporation. Poultry Science. 1998;77:299–302. - PubMed
-
- Hiroshi T, Hisako W, Yasushige O, Hyi-Man P, Tatsuo M. Human alkaline phosphatase expression and secretion into chicken eggs in vivo gene electroporration in the oviduct of laying hens. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2002;292:88–93. - PubMed
-
- Liu YB, Yu MZ, Shen XZ. The establishment of a temporary expression system in chicken oviduct epithelium. Developmental & Reproductive Biology. 2001;10(1):13–19.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

