Growth factor receptor binding protein 2-mediated recruitment of the RING domain of Cbl to the epidermal growth factor receptor is essential and sufficient to support receptor endocytosis
- PMID: 15635092
- PMCID: PMC551491
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-09-0832
Growth factor receptor binding protein 2-mediated recruitment of the RING domain of Cbl to the epidermal growth factor receptor is essential and sufficient to support receptor endocytosis
Abstract
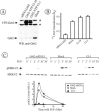
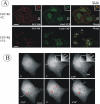
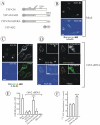
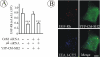
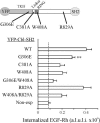
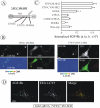
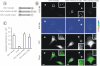
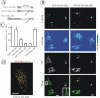
Knockdown of growth factor receptor binding protein 2 (Grb2) by RNA interference strongly inhibits clathrin-mediated endocytosis of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). To gain insights into the function of Grb2 in EGFR endocytosis, we have generated cell lines in which endogenous Grb2 was replaced by yellow fluorescent protein (YFP)-tagged Grb2 expressed at the physiological level. In these cells, Grb2-YFP fully reversed the inhibitory effect of Grb2 knockdown on EGFR endocytosis and, moreover, trafficked together with EGFR during endocytosis. Overexpression of Grb2-binding protein c-Cbl did not restore endocytosis in Grb2-depleted cells. However, EGFR endocytosis was rescued in Grb2-depleted cells by chimeric proteins consisting of the Src homology (SH) 2 domain of Grb2 fused to c-Cbl. The "knockdown and rescue" analysis revealed that the expression of Cbl-Grb2/SH2 fusions containing RING finger domain of Cbl restores normal ubiquitylation and internalization of the EGFR in the absence of Grb2, consistent with the important role of the RING domain in EGFR endocytosis. In contrast, the carboxy-terminal domain of Cbl, when attached to Grb2 SH2 domain, had 4 times smaller endocytosis-rescue effect compared with the RING-containing chimeras. Together, the data suggest that the interaction of Cbl carboxy terminus with CIN85 has a minor and a redundant role in EGFR internalization. We concluded that Grb2-mediated recruitment of the functional RING domain of Cbl to the EGFR is essential and sufficient to support receptor endocytosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor internalization through clathrin-coated pits requires Cbl RING finger and proline-rich domains but not receptor polyubiquitylation.Traffic. 2003 Aug;4(8):529-43. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2003.t01-1-00109.x. Traffic. 2003. PMID: 12839496
-
Ubiquitin ligase activity of c-Cbl guides the epidermal growth factor receptor into clathrin-coated pits by two distinct modes of Eps15 recruitment.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 31;279(53):55465-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409765200. Epub 2004 Oct 1. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15465819
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation of Cbl upon epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulation and its association with EGF receptor and downstream signaling proteins.J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 14;271(24):14554-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.24.14554. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8662998
-
Internalization of the epidermal growth factor receptor: role in signalling.Biochem Soc Trans. 2001 Aug;29(Pt 4):480-4. doi: 10.1042/bst0290480. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001. PMID: 11498013 Review.
-
Endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ErbBs.Exp Cell Res. 2008 Oct 15;314(17):3093-106. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.08.013. Epub 2008 Aug 28. Exp Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18793634 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EGF receptor ubiquitination is not necessary for its internalization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 23;104(43):16904-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707416104. Epub 2007 Oct 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17940017 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor exposed to cigarette smoke is aberrantly activated and undergoes perinuclear trafficking.FASEB J. 2008 Mar;22(3):910-7. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-7729com. Epub 2007 Oct 30. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 17971399 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation sites Ser991 and Tyr998 are implicated in the regulation of receptor endocytosis and phosphorylations at Ser1039 and Thr1041.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009 Sep;8(9):2131-44. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900148-MCP200. Epub 2009 Jun 15. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19531499 Free PMC article.
-
Endocytosis of Ubiquitylation-Deficient EGFR Mutants via Clathrin-Coated Pits is Mediated by Ubiquitylation.Traffic. 2015 Nov;16(11):1137-54. doi: 10.1111/tra.12314. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Traffic. 2015. PMID: 26251007 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of EGFR and Notch signaling by distinct isoforms of D-cbl during Drosophila development.Dev Biol. 2010 Jun 1;342(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.03.005. Epub 2010 Mar 17. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20302857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn, S., Kim, J., Lucaveche, C. L., Reedy, M. C., Luttrell, L. M., Lefkowitz, R. J., and Daaka, Y. (2002). Src-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation regulates dynamin self-assembly and ligand-induced endocytosis of the EGF receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 26642-26651. - PubMed
-
- Chang, C.-P., et al. (1993). Ligand-induced internalization of the EGF receptor is mediated by multiple endocytic codes analogous to the tyrosine motif found in constitutively internalized receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 19312-19320. - PubMed
-
- Chattopadhyay, A., Vecchi, M., Ji, Q., Mernaugh, R., and Carpenter, G. (1999). The role of individual SH2 domains in mediating association of phospholipase C-gamma1 with the activated EGF receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 26091-26097. - PubMed
-
- Chen, W. S., Lazar, C. S., Lund, K. A., Welsh, J. B., Chang, C. P., Walton, G. M., Der, C. J., Wiley, H. S., Gill, G. N., and Rosenfeld, M. G. (1989). Functional independence of the epidermal growth factor receptor from a domain required for ligand-induced internalization and calcium regulation. Cell 59, 33-43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

