Structural basis of filopodia formation induced by the IRSp53/MIM homology domain of human IRSp53
- PMID: 15635447
- PMCID: PMC545821
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600535
Structural basis of filopodia formation induced by the IRSp53/MIM homology domain of human IRSp53
Abstract
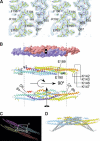
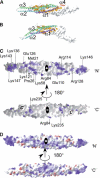
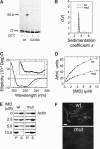
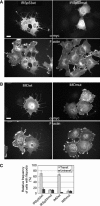
The scaffolding protein insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate p53 (IRSp53), a ubiquitous regulator of the actin cytoskeleton, mediates filopodia formation under the control of Rho-family GTPases. IRSp53 comprises a central SH3 domain, which binds to proline-rich regions of a wide range of actin regulators, and a conserved N-terminal IRSp53/MIM homology domain (IMD) that harbours F-actin-bundling activity. Here, we present the crystal structure of this novel actin-bundling domain revealing a coiled-coil domain that self-associates into a 180 A-long zeppelin-shaped dimer. Sedimentation velocity experiments confirm the presence of a single molecular species of twice the molecular weight of the monomer in solution. Mutagenesis of conserved basic residues at the extreme ends of the dimer abrogated actin bundling in vitro and filopodia formation in vivo, demonstrating that IMD-mediated actin bundling is required for IRSp53-induced filopodia formation. This study promotes an expanded view of IRSp53 as an actin regulator that integrates scaffolding and effector functions.
Figures

References
-
- Amann KJ, Renley BA, Ervasti JM (1998) A cluster of basic repeats in the dystrophin rod domain binds F-actin through an electrostatic interaction. J Biol Chem 273: 28419–28423 - PubMed
-
- Bakolitsa C, Cohen DM, Bankston LA, Bobkov AA, Cadwell GW, Jennings L, Critchley DR, Craig SW, Liddington RC (2004) Structural basis for vinculin activation at sites of cell adhesion. Nature 430: 583–586 - PubMed
-
- Bakolitsa C, de Pereda JM, Bagshaw CR, Critchley DR, Liddington RC (1999) Crystal structure of the vinculin tail suggests a pathway for activation. Cell 99: 603–613 - PubMed
-
- Bear JE, Svitkina TM, Krause M, Schafer DA, Loureiro JJ, Strasser GA, Maly IV, Chaga OY, Cooper JA, Borisy GG, Gertler FB (2002) Antagonism between Ena/VASP proteins and actin filament capping regulates fibroblast motility. Cell 109: 509–521 - PubMed
-
- Bockmann J, Kreutz MR, Gundelfinger ED, Bockers TM (2002) ProSAP/Shank postsynaptic density proteins interact with insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate IRSp53. J Neurochem 83: 1013–1017 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

