Identification of neuromedin S and its possible role in the mammalian circadian oscillator system
- PMID: 15635449
- PMCID: PMC545815
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600526
Identification of neuromedin S and its possible role in the mammalian circadian oscillator system
Abstract
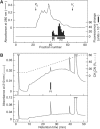
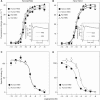
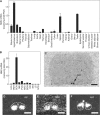
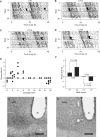
The discovery of neuropeptides has resulted in an increased understanding of novel regulatory mechanisms of certain physiological phenomena. Here we identify a novel neuropeptide of 36 amino-acid residues in rat brain as an endogenous ligand for the orphan G protein-coupled receptor FM-4/TGR-1, which was identified to date as the neuromedin U (NMU) receptor, and designate this peptide 'neuromedin S (NMS)' because it is specifically expressed in the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) of the hypothalamus. NMS shares a C-terminal core structure with NMU. The NMS precursor contains another novel peptide. NMS mRNA is highly expressed in the central nervous system, spleen and testis. In rat brain, NMS expression is restricted to the core of the SCN and has a diurnal peak under light/dark cycling, but remains stable under constant darkness. Intracerebroventricular administration of NMS in rats activates SCN neurons and induces nonphotic type phase shifts in the circadian rhythm of locomotor activity. These findings suggest that NMS in the SCN is implicated in the regulation of circadian rhythms through autocrine and/or paracrine actions.
Figures


References
-
- Barsh GS, Farooqi IS, O'Rahilly S (2000) Genetics of body-weight regulation. Nature 404: 644–651 - PubMed
-
- Brown DR, Quito FL (1988) Neuromedin U octapeptide alters ion transport in porcine jejunum. Eur J Pharmacol 155: 159–162 - PubMed
-
- Castel M, Belenky M, Cohen S, Wagner S, Schwartz WJ (1997) Light-induced c-Fos expression in the mouse suprachiasmatic nucleus: immunoelectron microscopy reveals co-localization in multiple cell types. Eur J Neurosci 9: 1950–1960 - PubMed
-
- Cheng MY, Bullock CM, Li C, Lee AG, Bermak JC, Belluzzi J, Weaver DR, Leslie FM, Zhou QY (2002) Prokineticin 2 transmits the behavioural circadian rhythm of the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Nature 417: 405–410 - PubMed
-
- Chu C, Jin Q, Kunitake T, Kato K, Nabekura T, Nakazato M, Kangawa K, Kannan H (2002) Cardiovascular actions of central neuromedin U in conscious rats. Regul Peptides 105: 29–34 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

