Dissecting the molecular control of endothelial NO synthase by caveolin-1 using cell-permeable peptides
- PMID: 15637154
- PMCID: PMC545535
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0407224102
Dissecting the molecular control of endothelial NO synthase by caveolin-1 using cell-permeable peptides
Abstract
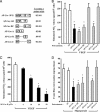
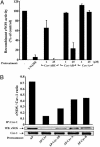
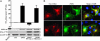
In endothelia, NO is synthesized by endothelial NO synthase (eNOS), which is negatively regulated by caveolin-1 (Cav-1), the primary coat protein of caveolae. We show that delivery of Cav-1 amino acids 82-101 (Cav) fused to an internalization sequence from Antennapedia (AP) blocks NO release in vitro and inflammation and tumor angiogenesis in vivo. To characterize the molecular mechanism by which the AP-Cav peptide and Cav-1 mediate eNOS inhibition, we subdivided the Cav portion of AP-Cav into three domains (Cav-A, -B, and -C), synthesized five overlapping peptides (AP-Cav-A, -AB, -B, -BC, and -C), and tested their effects on eNOS-dependent activities. Peptides containing the Cav-B domain (amino acids 89-95) induced time- and dose-dependent inhibition of eNOS-dependent NO release in cultured endothelial cells, NO-dependent inflammation in the ear, and hydraulic conductivity in isolated venules. Alanine scanning of AP-Cav-B revealed that Thr-90 and -91 (T90,91) and Phe-92 (F92) are crucial for AP-Cav-B- and AP-Cav-mediated inhibition of eNOS. Mutation of F92 to A92 in the Cav-1 cDNA caused the loss of eNOS inhibitory activity compared with wild-type Cav-1. These data highlight the importance of amino acids 89-95 and particularly F92 in mediating eNOS inhibition by AP-Cav and Cav-1.
Figures


References
-
- Gratton, J. P., Bernatchez, P. N. & Sessa, W. C. (2004) Circ. Res. 94, 1408-1417. - PubMed
-
- Shaul, P. W., Smart, E. J., Robinson, L. J., German, Z., Yuhanna, I. S., Ying, Y., Anderson, R. G. & Michel, T. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271, 6518-6522. - PubMed
-
- Drab, M., Verkade, P., Elger, M., Kasper, M., Lohn, M., Lauterbach, B., Menne, J., Lindschau, C., Mende, F., Luft, F. C., et al. (2001) Science 293, 2449-2452. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL64793/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064793/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HV-28186/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL057665/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL072618/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 57665/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL 70295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL061371/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL070295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL 61371/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HV028186/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

