Purification and characterization of a novel class IIa bacteriocin, piscicocin CS526, from surimi-associated Carnobacterium piscicola CS526
- PMID: 15640235
- PMCID: PMC544203
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.71.1.554-557.2005
Purification and characterization of a novel class IIa bacteriocin, piscicocin CS526, from surimi-associated Carnobacterium piscicola CS526
Abstract
The bacteriocin piscicocin CS526 was inactivated by proteolytic enzymes, was stable at 100 degrees C for 30 min, had a pH range of 2 to 8, and was active against Enterococcus, Listeria, Pediococcus, and Leuconostoc. The N-terminal sequence was YGNGL, not the YGNGV consensus motif common in class IIa bacteriocins (alternate residues underlined). The molecular mass of piscicocin CS526, which had a bactericidal mode of action, was approximately 4,430 Da.
Figures

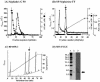
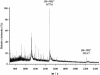
References
-
- Atrih, A., N. Rekhif, A. J. G. Moir, A. Lebrihi, and G. Lefebvre. 2001. Mode of action, purification and amino acid sequence of plantaricin C19, an anti-Listeria bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus plantarum C19. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 68:93-104. - PubMed
-
- Bennik, M. H. J., B. Vanloo, R. Brasseur, L. G. M. Gorris, and E. J. Smid. 1998. A novel bacteriocin with a YGNGV motif from vegetable-associated Enterococcus mundtii: full characterization and interaction with target organisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1373:47-58. - PubMed
-
- Bhugaloo-Vial, P., X. Dousset, A. Metivier, O. Sorokine, P. Anglade, P. Boyaval, and D. Marion. 1996. Purification and amino acid sequences of piscicocins V1a and V1b, two class IIa bacteriocins secreted by Carnobacterium piscicola V1 that display significantly different levels of specific inhibitory activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62:4410-4416. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhunia, A. K., M. C. Johnson, and B. Ray. 1987. Direct detection of an antimicrobial peptide of Pediococcus acidilactici in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J. Ind. Microbiol. 2:319-322.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

