Imaging in situ breast carcinoma (with or without an invasive component) with technetium-99m pentavalent dimercaptosuccinic acid and technetium-99m 2-methoxy isobutyl isonitrile scintimammography
- PMID: 15642168
- PMCID: PMC1064097
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr948
Imaging in situ breast carcinoma (with or without an invasive component) with technetium-99m pentavalent dimercaptosuccinic acid and technetium-99m 2-methoxy isobutyl isonitrile scintimammography
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of the study was to retrospectively define specific features of the technetium-99m pentavalent dimercaptosuccinic acid (99mTc-(V)DMSA) and technetium-99m 2-methoxy isobutyl isonitrile (99mTc-Sestamibi [99mTc-MIBI]) distribution in ductal breast carcinoma in situ and lobular breast carcinoma in situ (DCIS/LCIS), in relation to mammographic, histological and immunohistochemical parameters.
Materials and methods: One hundred and two patients with suspicious palpation or mammographic findings were submitted preoperatively to scintimammography (a total of 72 patients with 99mTc-(V)DMSA and a total of 75 patients with 99mTc-Sestamibi, 45 patients receiving both radiotracers). Images were acquired at 10 min and 60 min, and were evaluated for a pattern of diffuse radiotracer accumulation. The tumor-to-background ratios were correlated (T-pair test) with mammographic, histological and immunohistochemical characteristics.
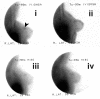
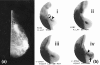
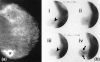
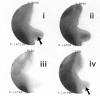
Results: Histology confirmed malignancy in 46/102 patients: 20/46 patients had DCIS/LCIS, with or without coexistent invasive lesions, and 26/46 patients had isolated invasive carcinomas. Diffuse 99mTc-(V)DMSA accumulation was noticed in 18/19 cases and 99mTc-Sestamibi in 6/13 DCIS/LCIS cases. Epithelial hyperplasia demonstrated a similar accumulation pattern. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value and negative predictive value for each tracer were calculated. Solely for 99mTc-(V)DMSA, the tumor-to-background ratio was significantly higher at 60 min than at 10 min and the diffuse uptake was significantly associated with suspicious microcalcifications, with the cell proliferation index > or = 40% and with c-erbB-2 > or = 10%.
Conclusion: 99mTc-(V)DMSA showed high sensitivity and 99mTc-Sestamibi showed high specificity in detecting in situ breast carcinoma (99mTc-(V)DMSA especially in cases with increased cell proliferation), and these radiotracers could provide clinicians with preoperative information not always obtainable by mammography.
Figures



Similar articles
-
99mTc-(V)DMSA scintimammography in the assessment of breast lesions: comparative study with 99mTc-MIBI.Eur J Nucl Med. 2001 Jul;28(7):923-8. doi: 10.1007/s002590100545. Eur J Nucl Med. 2001. PMID: 11504092
-
Uptake and washout of 99mTcV-dimercaptosuccinic acid and 99mTc-sestamibi in the assessment of histological type and grade in breast cancer.Nucl Med Commun. 2002 May;23(5):461-7. doi: 10.1097/00006231-200205000-00006. Nucl Med Commun. 2002. PMID: 11973487
-
The potential role of Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) in breast carcinogenesis and its correlation with 99mTc-(V)DMSA scintimammography.Am J Clin Oncol. 2007 Aug;30(4):420-7. doi: 10.1097/COC.0b013e3180337792. Am J Clin Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17762443
-
Dynamic imaging: scintimammography.Eur J Radiol. 1998 May;27 Suppl 2:S259-64. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(98)00072-2. Eur J Radiol. 1998. PMID: 9652532 Review.
-
Carcinoma in situ of the female breast. A clinico-pathological, immunohistological, and DNA ploidy study.APMIS Suppl. 2003;(108):1-67. APMIS Suppl. 2003. PMID: 12874968 Review.
Cited by
-
Pentavalent technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid [99m Tc-(V)DMSA] brain scintitomography--a plausible non-invasive depicter of glioblastoma proliferation and therapy response.J Neurooncol. 2007 Dec;85(3):291-5. doi: 10.1007/s11060-007-9410-7. Epub 2007 Jun 7. J Neurooncol. 2007. PMID: 17554495
-
In vitro verification of the correlation of in vivo 99mTc-(V)DMSA uptake with cellular proliferation rate.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005 Oct;32(10):1240-1. doi: 10.1007/s00259-005-1860-6. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005. PMID: 16025274 No abstract available.
-
Association of mammographic density with pathologic findings.Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2013 Dec;15(12):e16698. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.16698. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2013. PMID: 24693404 Free PMC article.
-
THE ROLE OF TUMOR-SEEKING RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS IN THE DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF ADRENAL TUMORS.Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2020 Jul-Sep;16(3):316-323. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2020.316. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2020. PMID: 33363653 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of tracer 99mTc(V)-DMSA uptake as a measure of tumor cell proliferation in vitro.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054361. Epub 2013 Jan 15. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23335999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schnitt SJ, Connolly JL, Recht A, Silver B, Harris JR. Breast relapse following primary radiation therapy for early breast cancer. II. Detection, pathologic features and prognostic significance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1985;11:1277–1284. - PubMed
-
- Bartelink H, Borger JH, van Dongen JA, Peterse JL. The impact of tumor size and histology on local control after breast conserving treatment. Radiother Oncol. 1988;11:297–303. - PubMed
-
- Khalkhali I, Mena I, Jouanne E, Diggles L, Venegas R, Block J, Alle K, Klein S. Prone scintimammography in patients with suspicion of carcinoma of the breast. J Am Coll Surg. 1994;178:491–497. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

