Human embryonal epithelial cells of the developing small intestinal crypts can express the Hodgkin-cell associated antigen Ki-1 (CD30) in spontaneous abortions during the first trimester of gestation
- PMID: 15644135
- PMCID: PMC546234
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4682-2-1
Human embryonal epithelial cells of the developing small intestinal crypts can express the Hodgkin-cell associated antigen Ki-1 (CD30) in spontaneous abortions during the first trimester of gestation
Abstract
Background: Ki-1 (CD30) antigen expression is not found on peripheral blood cells but its expression can be induced in vitro on T and B lymphocytes by viruses and lectins. Expression of CD30 in normal tissues is very limited, being restricted mainly to a subpopulation of large lymphoid cells; in particular, cells of the recently described anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL), the Reed-Sternberg (RS) cells of Hodgkin's lymphoma and scattered large parafollicular cells in normal lymphoid tissues. More recent reports have described CD30 expression in non-hematopoietic and malignant cells such as cultured human macrophages, human decidual cells, histiocytic neoplastic cells, mesothelioma cells, embryonal carcinoma and seminoma cells.
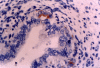
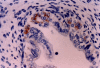
Results: We investigated the immunohistochemical expression of CD30 antigen in 15 paraffin-embedded tissue samples representing small intestines from fetuses after spontaneous abortion in the 8th, 10th and 12th weeks using the monoclonal antibody Ki-1. Hormones had been administered to all our pregnant women to support gestation. In addition, a panel of monoclonal antibodies was used to identify leukocytes (CD45/LCA), B-lymphocytes (CD20/L-26) and T-lymphocytes (CD3). Our findings were correlated with those obtained simultaneously from intestinal tissue samples obtained from 15 fetuses after therapeutic or voluntary abortions.
Conclusions: The results showed that: (1) epithelial cells in the developing intestinal crypts express the CD30 (Ki-1) antigen; (2) CD30 expression in these epithelial cells is higher in cases of hormonal administration than in normal gestation. In the former cases (hormonal support of gestation) a mild mononuclear intraepithelial infiltrate composed of CD3 (T-marker)-positive cells accompanies the CD30-positive cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human decidual cells can express the Hodgkin's cell-associated antigen Ki-1 (CD30) in spontaneous abortions during the first trimester of gestation.Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2001;28(4):225-8. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 2001. PMID: 11838744
-
Imbalance of mononuclear cell infiltrates in the placental tissue from foetuses after spontaneous abortion versus therapeutic termination from 8th to 12th weeks of gestational age.Clin Exp Med. 2006 Dec;6(4):171-6. doi: 10.1007/s10238-006-0111-x. Clin Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 17191109
-
CD30 (Ki-1) molecule expression in human embryonal epithelial cells of the basal layer of the developing epidermis and epidermal buds and its potential significance for embryogenesis.Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2005 Sep;14(3):85-90, 92. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2005. Retraction in: Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2009 Sep;18(3):144. PMID: 16200333 Retracted.
-
CD30 in normal and neoplastic cells.Clin Immunol. 1999 Feb;90(2):157-64. doi: 10.1006/clim.1998.4636. Clin Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10080826 Review.
-
CD30: expression and function in health and disease.Semin Immunol. 1998 Dec;10(6):457-70. doi: 10.1006/smim.1998.0156. Semin Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9826579 Review.
Cited by
-
Ber-H2 (CD30) immunohistochemical staining of human fetal tissues.Int J Biol Sci. 2005;1(4):135-40. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.1.135. Epub 2005 Oct 1. Int J Biol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16244703 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith CA, Gruss HJ, Davis T, Anderson D, Farrah T, Baker E, Sutherland GR, Brannan CI, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Grabstein KH, Gliniak B, McAlister IB, Fanslow W, Alderson M, Falk B, Gimpel S, Gillis S, Din WS, Goodwin RG, Armitage RJ. CD30 antigen, a marker for Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a receptor whose ligand defines an emerging family of cytokines with homology to TNF. Cell. 1993;73:1349–1360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90361-S. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stein H, Mason DY, Gerdes J, O'Connor N, Wainscoat J, Pallesen G, Gatter K, Falini B, Delsol G, Lemke H, Schwarting R, Lennert K. The expression of the Hodgkin's disease-associated antigen Ki-1 in reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: evidence that Reed-Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from activated lymphoid cells. Blood. 1985;66:848–858. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

