Involvement of Sir2/4 in silencing of DNA breakage and recombination on mouse YACs during yeast meiosis
- PMID: 15647382
- PMCID: PMC551506
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-07-0592
Involvement of Sir2/4 in silencing of DNA breakage and recombination on mouse YACs during yeast meiosis
Abstract
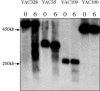
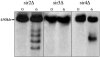
Yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs) that contain human DNA backbone undergo DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) and recombination during yeast meiosis at rates similar to the yeast native chromosomes. Surprisingly, YACs containing DNA covering a recombination hot spot in the mouse major histocompatibility complex class III region do not show meiotic DSBs and undergo meiotic recombination at reduced levels. Moreover, segregation of these YACs during meiosis is seriously compromised. In meiotic yeast cells carrying the mutations sir2 or sir4, but not sir3, these YACs show DSBs, suggesting that a unique chromatin structure of the YACs, involving Sir2 and Sir4, protects the YACs from the meiotic recombination machinery. We speculate that the paucity of DSBs and recombination events on these YACs during yeast meiosis may reflect the refractory nature of the corresponding region in the mouse genome.
Figures
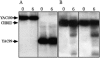
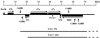
Similar articles
-
Double-strand breaks on YACs during yeast meiosis may reflect meiotic recombination in the human genome.Nat Genet. 1996 Aug;13(4):481-4. doi: 10.1038/ng0896-481. Nat Genet. 1996. PMID: 8696347
-
An implanted recombination hot spot stimulates recombination and enhances sister chromatid cohesion of heterologous YACs during yeast meiosis.Genetics. 1994 Dec;138(4):1055-65. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.4.1055. Genetics. 1994. PMID: 7896090 Free PMC article.
-
Sir2 silences gene transcription by targeting the transition between RNA polymerase II initiation and elongation.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;28(12):3979-94. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00019-08. Epub 2008 Apr 7. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18391020 Free PMC article.
-
Stay close to your sister.Mol Cell. 2004 May 21;14(4):418-20. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(04)00266-7. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15149590 Review.
-
The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases.Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:417-35. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073651. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15189148 Review.
Cited by
-
Separation of roles of Zip1 in meiosis revealed in heterozygous mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Genet Genomics. 2009 Nov;282(5):453-62. doi: 10.1007/s00438-009-0477-z. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Mol Genet Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19714362
-
Loss of a histone deacetylase dramatically alters the genomic distribution of Spo11p-catalyzed DNA breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Mar 6;104(10):3955-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0700412104. Epub 2007 Feb 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17360459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borde, V., Goldman, A., and Lichten, M. (2000). Direct coupling between meiotic DNA replication and recombination initiation. Science 290, 806-809. - PubMed
-
- Burke, D., and Olson, M. (1991). Preparation of clone libraries in yeast artificial-chromosome vectors. Methods Enzymol. 194, 251-270. - PubMed
-
- Cervantes, M., Farah, J., and Smith, G. (2000). Meiotic DNA breaks associated with recombination in S. pombe. Mol. Cell 5, 883-888. - PubMed
-
- Gasser, S., and Cockell, M. (2001). The molecular biology of the SIR proteins. Gene 279, 1-16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

