Activity-dependent presynaptic regulation of quantal size at the mammalian neuromuscular junction in vivo
- PMID: 15647477
- PMCID: PMC6725499
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3252-04.2005
Activity-dependent presynaptic regulation of quantal size at the mammalian neuromuscular junction in vivo
Abstract
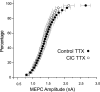
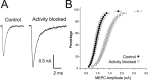
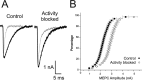
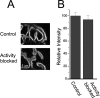
Changes in synaptic activity alter quantal size, but the relative roles of presynaptic and postsynaptic cells in these changes are only beginning to be understood. We examined the mechanism underlying increased quantal size after block of synaptic activity at the mammalian neuromuscular junction in vivo. We found that changes in neither acetylcholinesterase activity nor acetylcholine receptor density could account for the increase. By elimination, it appears likely that the site of increased quantal size after chronic block of activity is presynaptic and involves increased release of acetylcholine. We used mice with muscle hyperexcitability caused by mutation of the ClC-1 muscle chloride channel to examine the role of postsynaptic activity in controlling quantal size. Surprisingly, quantal size was increased in ClC mice before block of synaptic activity. We examined the mechanism underlying increased quantal size in ClC mice and found that it also appeared to be located presynaptically. When presynaptic activity was completely blocked in both control and ClC mice, quantal size was large in both groups despite the higher level of postsynaptic activity in ClC mice. This suggests that postsynaptic activity does not regulate quantal size at the neuromuscular junction. We propose that presynaptic activity modulates quantal size at the neuromuscular junction by modulating the amount of acetylcholine released from vesicles.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TGF-beta2 alters the characteristics of the neuromuscular junction by regulating presynaptic quantal size.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jul 27;107(30):13515-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1001695107. Epub 2010 Jul 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20624974 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent regulation of the binomial parameters p and n at the mouse neuromuscular junction in vivo.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Nov;104(5):2352-8. doi: 10.1152/jn.00460.2010. Epub 2010 Aug 25. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20739593 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Deficits at Neuromuscular Junctions in Two Mouse Models of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Type 2d.J Neurosci. 2016 Mar 16;36(11):3254-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1762-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26985035 Free PMC article.
-
Fast flies take a quantum leap.Neuron. 2006 Jun 1;50(5):667-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.05.011. Neuron. 2006. PMID: 16731505 Review.
-
Origin of quantal size variation and high-frequency miniature postsynaptic currents at the Caenorhabditis elegans neuromuscular junction.J Neurosci Res. 2010 Dec;88(16):3425-32. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22468. Epub 2010 Aug 18. J Neurosci Res. 2010. PMID: 20722072 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Depolarization-induced Ca2+ entry preferentially evokes release of large quanta in the developing Xenopus neuromuscular junction.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Nov;104(5):2730-40. doi: 10.1152/jn.01041.2009. Epub 2010 Sep 15. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20844112 Free PMC article.
-
Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity of Miniature Excitatory Postsynaptic Currents in Mouse Cortical Cultures Requires Neuronal Rab3A.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 21:2023.06.14.544980. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.14.544980. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39071374 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Impaired activity-dependent plasticity of quantal amplitude at the neuromuscular junction of Rab3A deletion and Rab3A earlybird mutant mice.J Neurosci. 2011 Mar 9;31(10):3580-8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5278-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21389214 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-beta2 alters the characteristics of the neuromuscular junction by regulating presynaptic quantal size.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jul 27;107(30):13515-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1001695107. Epub 2010 Jul 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20624974 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of the CaV 1.1-ryanodine receptor complex in a rat model of critical illness myopathy.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Jun;300(6):R1384-91. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00032.2011. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21474431 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agbulut O, Noirez P, Beaumont F, Butler-Browne G (2003) Myosin heavy chain isoforms in postnatal muscle development of mice. Biol Cell 95: 399-406. - PubMed
-
- Argentieri TM, Aiken SP, Laxminarayan S, McArdle JJ (1992) Characteristics of synaptic transmission in reinnervating rat skeletal muscle. Pflügers Arch Eur J Physiol 421: 256-261. - PubMed
-
- Atwood HL, Karunanithi S (2002) Diversification of synaptic strength: presynaptic elements. Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 497-516. - PubMed
-
- Barstad JA, Lilleheil G (1968) Transversally cut diaphragm preparation from rat. An adjuvant tool in the study of the physiology and pharmacology of the myoneural junction. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 175: 373-390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
