L1-mediated branching is regulated by two ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM)-binding sites, the RSLE region and a novel juxtamembrane ERM-binding region
- PMID: 15647482
- PMCID: PMC2860578
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4097-04.2005
L1-mediated branching is regulated by two ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM)-binding sites, the RSLE region and a novel juxtamembrane ERM-binding region
Abstract
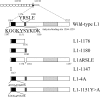
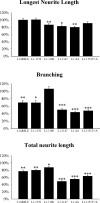
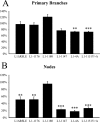
We investigated how the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 mediates neurite outgrowth through L1-L1 homophilic interactions. Wild-type L1 and L1 with mutations in the cytoplasmic domain (CD) were introduced into L1 knock-out neurons, and transfected neurons were grown on an L1 substrate. Neurite length and branching were compared between wild-type L1 and L1CD mutations. Surprisingly, the L1CD is not required for L1-mediated neurite outgrowth but plays a critical role in neurite branching, through both the juxtamembrane region and the RSLE region. We demonstrate that both regions serve as ezrin-moesin-radixin-binding sites. A truncation mutant that deletes 110 of 114 amino acids of the L1CD still supports neurite outgrowth on an L1 substrate, suggesting that a coreceptor binds to L1 in cis and mediates neurite outgrowth and that L1-ankyrin interactions are not essential for neurite initiation or outgrowth. These data are consistent with a model in which L1 can influence L1-mediated neurite outgrowth and branching through both the L1CD and a coreceptor.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pathological missense mutations of neural cell adhesion molecule L1 affect neurite outgrowth and branching on an L1 substrate.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004 Dec;27(4):522-30. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2004.08.005. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15555929
-
Interactions between the L1 cell adhesion molecule and ezrin support traction-force generation and can be regulated by tyrosine phosphorylation.J Neurosci Res. 2008 Sep;86(12):2602-14. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21705. J Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18478542 Free PMC article.
-
Binding partners L1 cell adhesion molecule and the ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM) proteins are involved in development and the regenerative response to injury of hippocampal and cortical neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2004 Sep;20(6):1436-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03620.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15355311
-
The interaction between L1-type proteins and ankyrins--a master switch for L1-type CAM function.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2009;14(1):57-69. doi: 10.2478/s11658-008-0035-4. Epub 2008 Oct 6. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2009. PMID: 18839070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of L1CAM for axon sprouting and branching.Cell Tissue Res. 2012 Jul;349(1):39-48. doi: 10.1007/s00441-012-1345-4. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Cell Tissue Res. 2012. PMID: 22370595 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential effects of human L1CAM mutations on complementing guidance and synaptic defects in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 14;8(10):e76974. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076974. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24155914 Free PMC article.
-
The activation of ezrin-radixin-moesin proteins is regulated by netrin-1 through Src kinase and RhoA/Rho kinase activities and mediates netrin-1-induced axon outgrowth.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Oct;22(19):3734-46. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-11-0917. Epub 2011 Aug 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21849478 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol inhibits L1 cell adhesion molecule tyrosine phosphorylation and dephosphorylation and activation of pp60(src).J Neurochem. 2009 Aug;110(3):779-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06143.x. Epub 2009 May 3. J Neurochem. 2009. PMID: 19457108 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of long-term exposure of SH-SY5Y cells to morphine: a whole cell proteomic analysis.Proteome Sci. 2006 Dec 21;4:23. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-4-23. Proteome Sci. 2006. PMID: 17184524 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of specific membrane lipid domains in EGF receptor activation and cell adhesion molecule stabilization in a developing olfactory system.PLoS One. 2009 Sep 29;4(9):e7222. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007222. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19787046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castellani V, Chedotal A, Schachner M, Faivre-Sarrailh C, Rougon G (2000) Analysis of the L1-deficient mouse phenotype reveals cross-talk between Sema3A and L1 signaling pathways in axonal guidance. Neuron 27: 237-249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
