Heterodimers of retinoic acid receptors and thyroid hormone receptors display unique combinatorial regulatory properties
- PMID: 15650024
- PMCID: PMC2675561
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2004-0210
Heterodimers of retinoic acid receptors and thyroid hormone receptors display unique combinatorial regulatory properties
Abstract
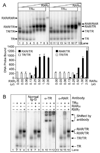
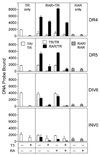
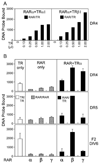
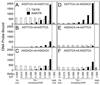
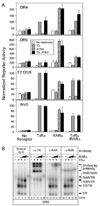
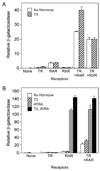
Nuclear receptors are ligand-regulated transcription factors that regulate key aspects of metazoan development, differentiation, and homeostasis. Nuclear receptors recognize target genes by binding to specific DNA recognition sequences, denoted hormone response elements (HREs). Many nuclear receptors can recognize HREs as either homodimers or heterodimers. Retinoid X receptors (RXRs), in particular, serve as important heterodimer partners for many other nuclear receptors, including thyroid hormone receptors (TRs), and RXR/TR heterodimers have been proposed to be the primary mediators of target gene regulation by T3 hormone. Here, we report that the retinoic acid receptors (RARs), a distinct class of nuclear receptors, are also efficient heterodimer partners for TRs. These RAR/TR heterodimers form with similar affinities as RXR/TR heterodimers on an assortment of consensus and natural HREs, and preferentially assemble with the RAR partner 5' of the TR moiety. The corepressor and coactivator recruitment properties of these RAR/TR heterodimers and their transcriptional activities in vivo are distinct from those observed with the corresponding RXR heterodimers. Our studies indicate that RXRs are not unique in their ability to partner with TRs, and that RARs can also serve as robust heterodimer partners and combinatorial regulators of T3-modulated gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Heterodimeric receptor complexes determine 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine and retinoid signaling specificities.Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jul;6(7):1153-62. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.7.1324421. Mol Endocrinol. 1992. PMID: 1324421
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and retinoic acid receptors differentially control the interactions of retinoid X receptor heterodimers with ligands, coactivators, and corepressors.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Apr;17(4):2166-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.4.2166. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9121466 Free PMC article.
-
The function of retinoid X receptors on negative thyroid hormone response elements.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997 Apr 4;128(1-2):85-96. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(97)04025-2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1997. PMID: 9140079
-
Hetero- and homodimeric receptors in thyroid hormone and vitamin A action.Receptor. 1993 Fall;3(3):183-91. Receptor. 1993. PMID: 8167569 Review.
-
[Genetic control of the development by retinoic acid].C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1997;191(1):77-90. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1997. PMID: 9181129 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Targeting Androgen, Thyroid Hormone, and Vitamin A and D Receptors to Treat Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 26;25(17):9245. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179245. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early thyroid hormone-induced gene expression changes in N2a-β neuroblastoma cells.J Mol Neurosci. 2011 Oct;45(2):76-86. doi: 10.1007/s12031-010-9389-y. Epub 2010 May 27. J Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 20506002
-
The p160 coactivator PAS-B motif stabilizes nuclear receptor binding and contributes to isoform-specific regulation by thyroid hormone receptors.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 17;284(29):19554-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.007542. Epub 2009 Jun 1. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19487700 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence and structural analysis of BTB domain proteins.Genome Biol. 2005;6(10):R82. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-10-r82. Epub 2005 Sep 15. Genome Biol. 2005. PMID: 16207353 Free PMC article.
-
Prepubertal testis development relies on retinoic acid but not rexinoid receptors in Sertoli cells.EMBO J. 2006 Dec 13;25(24):5816-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601447. Epub 2006 Nov 23. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 17124491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apriletti JW, Ribeiro RC, Wagner RL, Feng W, Webb P, Kushner PJ, West BL, Nilsson S, Scanlan TS, Fletterick RJ, Baxter JD. Molecular and structural biology of thyroid hormone receptors. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl. 1998;25:S2–S11. - PubMed
-
- Beato M, Klug J. Steroid hormone receptors: an update. Human Reprod Update. 2000;6:225–236. - PubMed
-
- Chambon P. A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 1996;10:940–954. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Lazar MA. The mechanism of action of thyroid hormones. Annu Rev Physiol. 2000;62:439–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

