Heterodimers of retinoic acid receptors and thyroid hormone receptors display unique combinatorial regulatory properties
- PMID: 15650024
- PMCID: PMC2675561
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2004-0210
Heterodimers of retinoic acid receptors and thyroid hormone receptors display unique combinatorial regulatory properties
Abstract
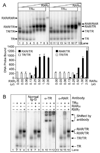
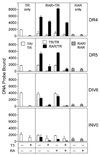
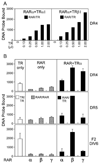
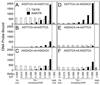
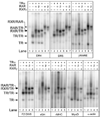
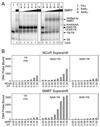
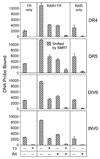
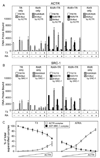
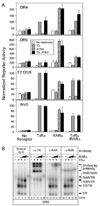
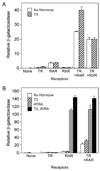
Nuclear receptors are ligand-regulated transcription factors that regulate key aspects of metazoan development, differentiation, and homeostasis. Nuclear receptors recognize target genes by binding to specific DNA recognition sequences, denoted hormone response elements (HREs). Many nuclear receptors can recognize HREs as either homodimers or heterodimers. Retinoid X receptors (RXRs), in particular, serve as important heterodimer partners for many other nuclear receptors, including thyroid hormone receptors (TRs), and RXR/TR heterodimers have been proposed to be the primary mediators of target gene regulation by T3 hormone. Here, we report that the retinoic acid receptors (RARs), a distinct class of nuclear receptors, are also efficient heterodimer partners for TRs. These RAR/TR heterodimers form with similar affinities as RXR/TR heterodimers on an assortment of consensus and natural HREs, and preferentially assemble with the RAR partner 5' of the TR moiety. The corepressor and coactivator recruitment properties of these RAR/TR heterodimers and their transcriptional activities in vivo are distinct from those observed with the corresponding RXR heterodimers. Our studies indicate that RXRs are not unique in their ability to partner with TRs, and that RARs can also serve as robust heterodimer partners and combinatorial regulators of T3-modulated gene expression.
Figures
References
-
- Apriletti JW, Ribeiro RC, Wagner RL, Feng W, Webb P, Kushner PJ, West BL, Nilsson S, Scanlan TS, Fletterick RJ, Baxter JD. Molecular and structural biology of thyroid hormone receptors. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl. 1998;25:S2–S11. - PubMed
-
- Beato M, Klug J. Steroid hormone receptors: an update. Human Reprod Update. 2000;6:225–236. - PubMed
-
- Chambon P. A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 1996;10:940–954. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Lazar MA. The mechanism of action of thyroid hormones. Annu Rev Physiol. 2000;62:439–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

