Human herpesvirus 6B induces cell cycle arrest concomitant with p53 phosphorylation and accumulation in T cells
- PMID: 15650224
- PMCID: PMC544083
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.3.1961-1965.2005
Human herpesvirus 6B induces cell cycle arrest concomitant with p53 phosphorylation and accumulation in T cells
Abstract
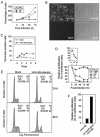
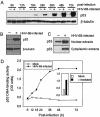
We studied the interactions between human herpesvirus 6B (HHV-6B) and its host cell. Productive infections of T-cell lines led to G1/S- and G2/M-phase arrest in the cell cycle concomitant with an increased level and enhanced DNA-binding activity of p53. More than 70% of HHV-6B-infected cells did not bind annexin V, indicating that the majority of cells were not undergoing apoptosis. HHV-6B infection induced Ser20 and Ser15 phosphorylation on p53, and the latter was inhibited by caffeine, an ataxia telangiectasia mutated kinase inhibitor. Thus, a productive HHV-6B infection suppresses T-cell proliferation concomitant with the phosphorylation and accumulation of p53.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The DR6 protein from human herpesvirus-6B induces p53-independent cell cycle arrest in G2/M.Virology. 2014 Mar;452-453:254-63. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.01.028. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24606703
-
IL-2-regulated persistent human herpesvirus-6B infection facilitates growth of adult T cell leukemia cells.J Med Dent Sci. 2005 Jun;52(2):135-41. J Med Dent Sci. 2005. PMID: 16187619
-
Human herpesvirus 6B inhibits cell proliferation by a p53-independent pathway.J Clin Virol. 2006 Dec;37 Suppl 1:S63-8. doi: 10.1016/S1386-6532(06)70014-2. J Clin Virol. 2006. PMID: 17276372
-
Estimating immunoregulatory gene networks in human herpesvirus type 6-infected T cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Oct 21;336(2):469-77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.08.104. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 16140273
-
Human herpesvirus 6 infection arrests cord blood mononuclear cells in G(2) phase of the cell cycle.FEBS Lett. 2004 Feb 27;560(1-3):25-9. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(04)00035-3. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 14987992
Cited by
-
Virus manipulation of cell cycle.Protoplasma. 2012 Jul;249(3):519-28. doi: 10.1007/s00709-011-0327-9. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Protoplasma. 2012. PMID: 21986922 Review.
-
Immunomodulation and immunosuppression by human herpesvirus 6A and 6B.Future Virol. 2013 Mar;8(3):273-287. doi: 10.2217/fvl.13.7. Future Virol. 2013. PMID: 24163703 Free PMC article.
-
Human herpesvirus 6 open reading frame U14 protein and cellular p53 interact with each other and are contained in the virion.J Virol. 2005 Oct;79(20):13037-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.20.13037-13046.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16189006 Free PMC article.
-
Human herpesvirus 6 suppresses T cell proliferation through induction of cell cycle arrest in infected cells in the G2/M phase.J Virol. 2011 Jul;85(13):6774-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02577-10. Epub 2011 Apr 27. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21525341 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus matrix protein induces lung epithelial cell cycle arrest through a p53 dependent pathway.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e38052. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038052. Epub 2012 May 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22662266 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agulnick, A. D., J. R. Thompson, S. Iyengar, G. Pearson, D. Ablashi, and R. P. Ricciardi. 1993. Identification of a DNA-binding protein of human herpesvirus 6, a putative DNA polymerase stimulatory factor. J. Gen. Virol. 74:1003-1009. - PubMed
-
- Black, J. B., C. Lopez, and P. E. Pellett. 1992. Induction of host cell protein synthesis by human herpesvirus 6. Virus Res. 22:13-23. - PubMed
-
- Blasina, A., B. D. Price, G. A. Turenne, and C. H. McGowan. 1999. Caffeine inhibits the checkpoint kinase ATM. Curr. Biol. 9:1135-1138. - PubMed
-
- Bonini, P., S. Cicconi, A. Cardinale, C. Vitale, A. L. Serafino, M. T. Ciotti, and L. N. Marlier. 2004. Oxidative stress induces p53-mediated apoptosis in glia: p53 transcription-independent way to die. J. Neurosci. Res. 75:83-95. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

