A method to attenuate pneumoperitoneum-induced reductions in splanchnic blood flow
- PMID: 15650635
- PMCID: PMC1356910
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000153034.54128.5e
A method to attenuate pneumoperitoneum-induced reductions in splanchnic blood flow
Abstract
Objective: To determine if increasing nitric oxide bioactivity by inclusion of ethyl nitrite (ENO) in the insufflation admixture would attenuate pneumoperitoneum-induced decreases in splanchnic perfusion.
Summary background data: Organ blood flow is reduced during pneumoperitoneum and can contribute to laparoscopy-associated morbidity and mortality. Previous attempts to control such decreases in flow have been ineffective.
Methods: Laser-Doppler flow probes were placed on the liver and right kidney of anesthetized pigs. After a baseline recording period, animals were insufflated to a final intraperitoneal pressure of 15 mm Hg. Group one received CO2 (standard practice), whereas group 2 received CO2 plus 100 ppm ENO. Insufflation was maintained for 60 minutes and then the abdomen was manually deflated; monitoring was continued for another 60 minutes.
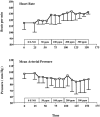
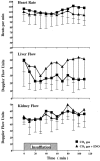
Results: CO2 insufflation (n = 5) cut liver blood flow in half; liver flow remained at this level throughout the postinsufflation period. Inclusion of 100 ppm ENO (n = 6) attenuated both the acute and prolonged blood flow decreases. Statistical modeling of the data showed that, on average, liver blood flow was 14.3 U/min higher in the ENO pigs compared with the CO2 group (P = 0.0454). In contrast, neither treatment significantly altered kidney blood flow (P = 0.6215).
Conclusion: The data indicate that ENO can effectively attenuate pneumoperitoneum-induced blood flow decreases within the peritoneal cavity. The result suggests a novel therapeutic method of regulating hemodynamic changes during laparoscopic procedures.
Figures
References
-
- Khaitan L, Holzman MD. Laparoscopic advances in general surgery. JAMA. 2002;287:1502–1505. - PubMed
-
- Taura P, Lopez A, Lacy AM, et al. Prolonged pneumoperitoneum at 15 mm Hg causes lactic acidosis. Surg Endosc. 1998;12:198–201. - PubMed
-
- Andrei VE, Schein M, Margolis M, et al. Liver enzymes are commonly elevated following laparoscopic cholecystectomy—is elevated intra-abdominal pressure the cause? Dig Surg. 1998;15:256–259. - PubMed
-
- Kotake Y, Takeda J, Matsumoto M, et al. Subclinical hepatic dysfunction in laparoscopic cholecystectomy and laparoscopic colectomy. Br J Anaesth. 2001;87:774–777. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

