XIAP inhibits caspase-3 and -7 using two binding sites: evolutionarily conserved mechanism of IAPs
- PMID: 15650747
- PMCID: PMC548652
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600544
XIAP inhibits caspase-3 and -7 using two binding sites: evolutionarily conserved mechanism of IAPs
Abstract
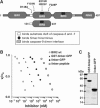
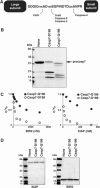
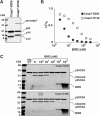
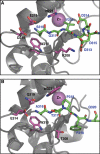
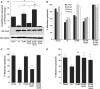
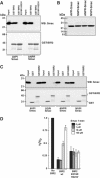
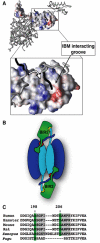
The X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) uses its second baculovirus IAP repeat domain (BIR2) to inhibit the apoptotic executioner caspase-3 and -7. Structural studies have demonstrated that it is not the BIR2 domain itself but a segment N-terminal to it that directly targets the activity of these caspases. These studies failed to demonstrate a role of the BIR2 domain in inhibition. We used site-directed mutagenesis of BIR2 and its linker to determine the mechanism of executioner caspase inhibition by XIAP. We show that the BIR2 domain contributes substantially to inhibition of executioner caspases. A surface groove on BIR2, which also binds to Smac/DIABLO, interacts with a neoepitope generated at the N-terminus of the caspase small subunit following activation. Therefore, BIR2 uses a two-site interaction mechanism to achieve high specificity and potency for inhibition. Moreover, for caspase-7, the precise location of the activating cleavage is critical for subsequent inhibition. Since apical caspases utilize this cleavage site differently, we predict that the origin of the death stimulus should dictate the efficiency of inhibition by XIAP.
Figures
References
-
- Barnhart BC, Peter ME (2002) Two faces of caspase-8. Nat Immunol 3: 896–898 - PubMed
-
- Bratton SB, Lewis J, Butterworth M, Duckett CS, Cohen GM (2002) XIAP inhibition of caspase-3 preserves its association with the Apaf-1 apoptosome and prevents CD95- and Bax-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 9: 881–892 - PubMed
-
- Chai J, Du C, Wu JW, Kyin S, Wang X, Shi Y (2000) Structural and biochemical basis of apoptotic activation by Smac/DIABLO. Nature 406: 855–862 - PubMed
-
- Chai J, Shiozaki E, Srinivasula SM, Wu Q, Datta P, Alnemri ES, Shi Y, Dataa P (2001) Structural basis of caspase-7 inhibition by XIAP. Cell 104: 769–780 - PubMed
-
- Chai J, Yan N, Huh JR, Wu JW, Li W, Hay BA, Shi Y (2003) Molecular mechanism of Reaper–Grim–Hid-mediated suppression of DIAP1-dependent Dronc ubiquitination. Nat Struct Biol 10: 892–898 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

