Effects of 5 alpha reductase inhibitors on androgen-dependent human prostatic carcinoma cells
- PMID: 15650886
- PMCID: PMC12161225
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-004-0632-1
Effects of 5 alpha reductase inhibitors on androgen-dependent human prostatic carcinoma cells
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the effects of MK906, a selective 5 alpha reductase (5alphaR) type 2 (5alphaR2) inhibitor, and of MK386, a specific 5alphaR1 inhibitor, on the cellular proliferation of androgen-dependent human prostatic cancer (PCa) cells in cultures of cells derived from bioptic and surgical tissues.
Methods: In this study we tested the effects of MK906 and MK386 in 30 cultures derived from PCa, 6 from PIN and 10 from benign prostatic hyperplasia specimens.
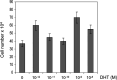
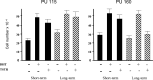
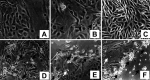
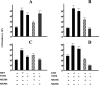
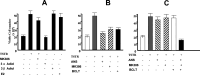
Results: Prostate primary cultures under short-term conditions (with <4 subcultures) represent a mixture of epithelial and stromal cells. Epithelial cells require testosterone (T) for optimal growth, but were not able to grow in the presence of T under long-term conditions even if DHT was able to induce cellular proliferation to a similar extent in both conditions, suggesting that 5alphaR can be lost in long-term cultures. Therefore, our studies were performed under short-term conditions. Both 5alphaR inhibitors decreased cell proliferation significantly and dose-dependently in all the samples tested. MK906 was more efficient than MK386 in 7 out of 10 cultures derived from BPH tissues, in 4 out of 6 cultures derived from PIN and in 18 out of 30 cultures derived from PCa. In 3 out of 10 BPH, in 2 out of 6 PIN and in 5 out of 30 PCa-derived cultures, both inhibitors presented similar efficacy, whereas in 1 out of 10 BPH and 7 out of 30 PCa-derived cultures MK386 was more efficient than MK906. In addition, MK386 was more efficient than MK906 in 4 out of 15 non-metastatic PCa and 2 out of 7 metastatic PCa-derived cultures.
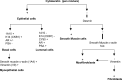
Conclusions: Considering that 5alphaR1 (responsible primarily for androgenic catabolism) is mostly expressed in epithelial cells and that 5alphaR2 (responsible for local DHT synthesis and release) is expressed in the stromal cells (which provides several paracrine growth factors and DHT itself to the epithelial cells), our experiments suggest that the inhibition of both 5alphaR1 and 5alphaR2 by MK386 and MK906, respectively, may have therapeutic potential in order to reduce the growth and progression of human prostatic cancers, through the inhibition of autocrine or paracrine mechanisms involving the stromal cell compartment. In addition, some effects of 5alphaR inhibitors could be mediated by estrogens, which are synthesized by the aromatase enzyme present in the epithelial cells. These aspects could be considered in order to improve the therapeutical management of PCa and for future clinical trials.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Finasteride for benign prostatic hyperplasia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Oct 6;2010(10):CD006015. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006015.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. PMID: 20927745 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions for hirsutism (excluding laser and photoepilation therapy alone).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Apr 28;2015(4):CD010334. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010334.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25918921 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- Akalu A, Dlmajian DA, Highshaw RA, Nichols PW, Reichardt JK (1999) Somatic mutations at the SRD5A2 locus encoding prostatic steroid 5alpha-reductase during prostate cancer progression. J Urol 161:1355–1358 - PubMed
-
- Asadi FK, Sharifi R (1995) Effects of sex steroids on cell growth and C-myc oncogene expression in LN-CaP and DU-145 prostatic carcinoma cell lines. Int Urol Nephrol 27:67–80 - PubMed
-
- Aumuller G, Eicheler W, Renneberg H, Adermann K, Vilja P, Forssmann WG (1996) Immunocytochemical evidence for differential subcellular localization of 5 alpha-reductase isoenzymes in human tissues. Acta Anat (Basel) 156:241–252 - PubMed
-
- Bologna M, Vicentini C, Festuccia C, Muzi P, Napolitano T, Biordi L, Miano L (1988) Short-term tissue culture of prostatic carcinoma samples provides useful biological parameters related to patient prognosis. Eur Urol 15:243–247 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

