Selection and characterization of a promoter for expression of single-copy recombinant genes in Gram-positive bacteria
- PMID: 15651989
- PMCID: PMC548306
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-5-3
Selection and characterization of a promoter for expression of single-copy recombinant genes in Gram-positive bacteria
Abstract
Background: In the past ten years there has been a growing interest in engineering Gram-positive bacteria for biotechnological applications, including vaccine delivery and production of recombinant proteins. Usually, bacteria are manipulated using plasmid expression vectors. The major limitation of this approach is due to the fact that recombinant plasmids are often lost from the bacterial culture upon removal of antibiotic selection. We have developed a genetic system based on suicide vectors on conjugative transposons allowing stable integration of recombinant DNA into the chromosome of transformable and non-transformable Gram-positive bacteria.
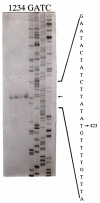
Results: The aim of this work was to select a strong chromosomal promoter from Streptococcus gordonii to improve this genetic system making it suitable for expression of single-copy recombinant genes. To achieve this task, a promoterless gene encoding a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (cat), was randomly integrated into the S. gordonii chromosome and transformants were selected for chloramphenicol resistance. Three out of eighteen chloramphenicol resistant transformants selected exhibited 100% stability of the phenotype and only one of them, GP215, carried the cat gene integrated as a single copy. A DNA fragment of 600 base pairs exhibiting promoter activity was isolated from GP215 and sequenced. The 5' end of its corresponding mRNA was determined by primer extention analysis and the putative -10 and a -35 regions were identified. To study the possibility of using this promoter (PP) for single copy heterologous gene expression, we created transcriptional fusions of PP with genes encoding surface recombinant proteins in a vector capable of integrating into the conjugative transposon Tn916. Surface recombinant proteins whose expression was controlled by the PP promoter were detected in Tn916-containing strains of S. gordonii and Bacillus subtilis after single copy chromosomal integration of the recombinant insertion vectors into the resident Tn916. The surface recombinant protein synthesized under the control of PP was also detected in Enterococcus faecalis after conjugal transfer of a recombinant Tn916 containing the transcriptional fusion.
Conclusion: We isolated and characterized a S. gordonii chromosomal promoter. We demonstrated that this promoter can be used to direct expression of heterologous genes in different Gram-positive bacteria, when integrated in a single copy into the chromosome.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Improved vectors for nisin-controlled expression in gram-positive bacteria.Plasmid. 2000 Sep;44(2):183-90. doi: 10.1006/plas.2000.1484. Plasmid. 2000. PMID: 10964628
-
Blue/white screening of recombinant plasmids in Gram-positive bacteria by interruption of alkaline phosphatase gene (phoZ) expression.Gene. 1998 Sep 28;219(1-2):91-9. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00396-5. Gene. 1998. PMID: 9757005
-
Autoregulation of subtilin biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis: the role of the spa-box in subtilin-responsive promoters.Peptides. 2004 Sep;25(9):1415-24. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2003.11.025. Peptides. 2004. PMID: 15374645
-
Engineering the gram-positive cell surface for construction of bacterial vaccine vectors.Methods. 1999 Sep;19(1):163-73. doi: 10.1006/meth.1999.0842. Methods. 1999. PMID: 10525453 Review.
-
Tn916-like genetic elements: a diverse group of modular mobile elements conferring antibiotic resistance.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011 Sep;35(5):856-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00283.x. Epub 2011 Jul 4. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21658082 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel algorithms reveal streptococcal transcriptomes and clues about undefined genes.PLoS Comput Biol. 2007 Jul;3(7):e132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030132. PLoS Comput Biol. 2007. PMID: 17616984 Free PMC article.
-
Overproduction of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens extracellular glutamyl-endopeptidase as a result of ectopic multi-copy insertion of an efficiently-expressed mpr gene into the Bacillus subtilis chromosome.Microb Cell Fact. 2011 Aug 5;10:64. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-10-64. Microb Cell Fact. 2011. PMID: 21819557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Medaglini D, Rush CM, Sestini P, Pozzi G. Commensal bacteria as vectors for mucosal vaccines against sexually transmitted diseases: vaginal colonization with recombinant streptococci induces local and systemic antibodies in mice. Vaccine. 1997;15:1330–1337. doi: 10.1016/S0264-410X(97)00026-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Magliani W, Conti S, Frazzi R, Pozzi G, Oggioni M, Polonelli L. Engineered commensal bacteria as delivery systems of anti-infective mucosal protectants. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2002;19:139–156. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

