Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of a multidisciplinary intervention programme to prevent new falls and functional decline among elderly persons at risk: design of a replicated randomised controlled trial [ISRCTN64716113]
- PMID: 15651990
- PMCID: PMC546206
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-5-6
Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of a multidisciplinary intervention programme to prevent new falls and functional decline among elderly persons at risk: design of a replicated randomised controlled trial [ISRCTN64716113]
Abstract
Background: Falls are common among community-dwelling elderly people and can have a considerable impact on quality of life and healthcare costs. People who have sustained a fall are at greater risk of falling again.We replicated a British randomised controlled trial which demonstrated the effectiveness of a multidisciplinary intervention programme to prevent falls. The objective is to describe the design of a replication study evaluating a multidisciplinary intervention programme on recurrent falls and functional decline among elderly persons at risk. The study consists of an effect evaluation, an economic evaluation and a process evaluation.
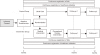
Methods/design: The programme is aimed at community-dwelling elderly people aged 65 years or over who have visited an accident and emergency department (A&E department) or a general practitioners' cooperative (GP cooperative) because of a fall. The design involves a two-group randomised controlled trial. Participants are followed for twelve months after baseline. The intervention programme consists of a detailed medical and occupational therapy assessment with referral to relevant services if indicated. People in the control group receive usual care. The main outcome measures of the effect evaluation are number of falls and daily functioning. The economic evaluation will be performed from a societal perspective. A process evaluation will be carried out to evaluate the feasibility of the intervention programme.
References
-
- Godlee F. Publishing study protocols: making them visible will improve registration, reporting and recruitment. BMC News and Views. 2001;2:4.
-
- Steenstra IA, Anema JR, Bongers PM, de Vet HC, van Mechelen W. Cost effectiveness of a multi-stage return to work program for workers on sick leave due to low back pain, design of a population based controlled trial [ISRCTN60233560] BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2003;4:26. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-4-26. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gillespie LD, Gillespie WJ, Robertson MC, Lamb SE, Cumming RG, Rowe BH. Interventions for preventing falls in elderly people. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003:CD000340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical