Assembly of lipoprotein particles containing apolipoprotein-B: structural model for the nascent lipoprotein particle
- PMID: 15653747
- PMCID: PMC1305374
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.046235
Assembly of lipoprotein particles containing apolipoprotein-B: structural model for the nascent lipoprotein particle
Abstract
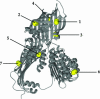
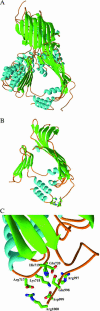
Apolipoprotein B (apoB) is the major protein component of large lipoprotein particles that transport lipids and cholesterol. We have developed a detailed model of the first 1000 residues of apoB using standard sequence alignment programs (ClustalW and MACAW) and the MODELLER6 package for three-dimensional homology modeling. The validity of the apoB model was supported by conservation of disulfide bonds, location of all proline residues in turns and loops, and conservation of the hydrophobic faces of the two C-terminal amphipathic beta-sheets, betaA (residues 600-763) and betaB (residues 780-1000). This model suggests a lipid-pocket mechanism for initiation of lipoprotein particle assembly. In a previous model we suggested that microsomal triglyceride transfer protein might play a structural role in completion of the lipid pocket. We no longer think this likely, but instead propose a hairpin-bridge mechanism for lipid pocket completion. Salt-bridges between four tandem charged residues (717-720) in the turn of the hairpin-bridge and four tandem complementary residues (997-1000) at the C-terminus of the model lock the bridge in the closed position, enabling the deposition of an asymmetric bilayer within the lipid pocket.
Figures








References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Carson, M. 1991. Ribbons 2.0. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24:958–961.
-
- Chatterton, J. E., M. L. Phillips, L. K. Curtiss, R. Milne, J. C. Fruchart, and V. N. Schumaker. 1995a. Immunoelectron microscopy of low density lipoproteins yields a ribbon and bow model for the conformation of apolipoprotein B on the lipoprotein surface. J. Lipid Res. 36:2027–2037. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

