Options for field diagnosis of human african trypanosomiasis
- PMID: 15653823
- PMCID: PMC544181
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.18.1.133-146.2005
Options for field diagnosis of human african trypanosomiasis
Abstract
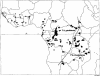
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) due to Trypanosoma brucei gambiense or T. b. rhodesiense remains highly prevalent in several rural areas of sub-Saharan Africa and is lethal if left untreated. Therefore, accurate tools are absolutely required for field diagnosis. For T. b. gambiense HAT, highly sensitive tests are available for serological screening but the sensitivity of parasitological confirmatory tests remains insufficient and needs to be improved. Screening for T. b. rhodesiense infection still relies on clinical features in the absence of serological tests available for field use. Ongoing research is opening perspectives for a new generation of field diagnostics. Also essential for both forms of HAT is accurate determination of the disease stage because of the high toxicity of melarsoprol, the drug most widely used during the neurological stage of the illness. Recent studies have confirmed the high accuracy of raised immunoglobulin M levels in the cerebrospinal fluid for the staging of T. b. gambiense HAT, and a promising simple assay (LATEX/IgM) is being tested in the field. Apart from the urgent need for better tools for the field diagnosis of this neglected disease, improved access to diagnosis and treatment for the population at risk remains the greatest challenge for the coming years.
Figures



References
-
- Aerts, D., P. True, L. Penchenier, Y. Claes, and D. Le Ray. 1992. A kit for in vitro isolation of trypanosomes in the field: first trial with sleeping sickness patients in the Congo Republic. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 86:394-395. - PubMed
-
- Aiyedun, B. A., A. A. Amodu, D. Bidwell, G. Bone, A. A. Buck, J. Coulm, J. L. Frezil, N. H. Kent, P. Mattern, A. R. Njogu, P. de Raadt, A. Voller, and M. Wery. 1976. Parallel evaluation of serological tests applied in African trypanosomiasis: a WHO collaborative study. Bull. W. H. O. 54:141-147. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akol, M. N., W. Olaho-Mukani, M. Odiit, J. C. Enyaru, E. Matovu, J. Magona, and N. D. Okitoi. 1999. Trypanosomosis agglutination card test for Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense sleeping sickness. East Afr. Med. J. 76:38-41. - PubMed
-
- Ancelle, T., A. Paugam, F. Bourlioux, A. Merad, and J. P. Vigier. 1997. Detection of trypanosomes in blood by the Quantitative Buffy Coat (QBC) technique: experimental evaluation. Med. Trop. 57:245-248. (In French.) - PubMed
-
- Asonganyi, T., F. Doua, S. N. Kibona, Y. M. Nyasulu, R. Masake, and F. Kuzoe. 1998. A multi-centre evaluation of the card indirect agglutination test for trypanosomiasis (TrypTect CIATT). Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 92:837-844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

