R1, a novel repressor of the human monoamine oxidase A
- PMID: 15654081
- PMCID: PMC2861901
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M410033200
R1, a novel repressor of the human monoamine oxidase A
Abstract
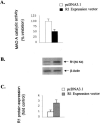
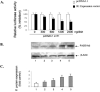
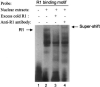
Monoamine oxidase catalyzes the oxidative deamination of a number of neurotransmitters. A deficiency in monoamine oxidase A results in aggressive behavior in both humans and mice. Studies on the regulation of monoamine oxidase A gene expression have shown that the Sp1 family is important for monoamine oxidase A expression. To search for novel transcription factors, the sequences of three Sp1 sites in the monoamine oxidase A core promoter were used in the yeast one-hybrid system to screen a human cDNA library. A novel repressor, R1 (RAM2), has been cloned. The R1 cDNA encodes a protein with 454 amino acids and an open reading frame at the 5'-end. The transfection of R1 in a human neuroblastoma cell line, SK-N-BE (2)-C, inhibited the monoamine oxidase A promoter and enzymatic activity. The degree of inhibition of monoamine oxidase A by R1 correlated with the level of R1 protein expression. R1 was also found to repress monoamine oxidase A promoter activity within a natural chromatin environment. A gel-shift assay indicated that the endogenous R1 protein in SK-N-BE (2)-C cells interacted with the R1 binding sequence. R1 also bound directly to the natural monoamine oxidase A promoter in vivo as shown by chromatin immunoprecipitation assay. Immunocytochemical analysis showed that R1 was expressed in both cytosol and nucleus, which suggested a role for R1 in transcriptional regulation. Northern blot analysis revealed the presence of endogenous R1 mRNA in human brain and peripheral tissues. Taken together, this study shows that R1 is a novel repressor that inhibits monoamine oxidase A gene expression.
Figures


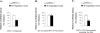
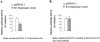


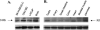
Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoid and androgen activation of monoamine oxidase A is regulated differently by R1 and Sp1.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jul 28;281(30):21512-21525. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600250200. Epub 2006 May 25. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16728402
-
Transcription factor E2F-associated phosphoprotein (EAPP), RAM2/CDCA7L/JPO2 (R1), and simian virus 40 promoter factor 1 (Sp1) cooperatively regulate glucocorticoid activation of monoamine oxidase B.Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;79(2):308-17. doi: 10.1124/mol.110.067439. Epub 2010 Oct 27. Mol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20980443 Free PMC article.
-
Dual functions of transcription factors, transforming growth factor-beta-inducible early gene (TIEG)2 and Sp3, are mediated by CACCC element and Sp1 sites of human monoamine oxidase (MAO) B gene.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 14;279(20):21021-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M312638200. Epub 2004 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15024015
-
Organization of MAO A and MAO B promoters and regulation of gene expression.Neurotoxicology. 2004 Jan;25(1-2):31-6. doi: 10.1016/S0161-813X(03)00113-X. Neurotoxicology. 2004. PMID: 14697878 Review.
-
Monoamine oxidases in major depressive disorder and alcoholism.Drug Discov Ther. 2012 Jun;6(3):112-22. Drug Discov Ther. 2012. PMID: 22890201 Review.
Cited by
-
Monoamine oxidase a expression is vital for embryonic brain development by modulating developmental apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 12;286(32):28322-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.241422. Epub 2011 Jun 22. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21697081 Free PMC article.
-
Type A monoamine oxidase; its unique role in mood, behavior and neurodegeneration.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2025 Mar;132(3):387-406. doi: 10.1007/s00702-024-02866-z. Epub 2024 Dec 2. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2025. PMID: 39621110 Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation and multiple functions of MAO genes.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2011 Jul;118(7):979-86. doi: 10.1007/s00702-010-0562-9. Epub 2011 Feb 27. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2011. PMID: 21359973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoamine oxidase A and repressor R1 are involved in apoptotic signaling pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jul 18;103(29):10923-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601515103. Epub 2006 Jul 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16829576 Free PMC article.
-
Rines E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates MAO-A levels and emotional responses.J Neurosci. 2013 Aug 7;33(32):12940-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5717-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23926250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shih JC. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1991;4:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Thorpe LW, Westlund KN, Kochersperger LM, Abell CW, Denney RM. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1987;35:23–32. - PubMed
-
- Johnston JP. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1968;17:1285–1297. - PubMed
-
- Knoll J, Magyar K. Adv. Biochem. Psychopharmacol. 1972;5:393–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

