Mycophenolate mofetil and roscovitine decrease cyclin expression and increase p27(kip1) expression in anti Thy1 mesangial proliferative nephritis
- PMID: 15654821
- PMCID: PMC1809292
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02684.x
Mycophenolate mofetil and roscovitine decrease cyclin expression and increase p27(kip1) expression in anti Thy1 mesangial proliferative nephritis
Abstract
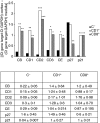
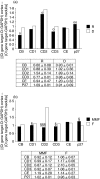
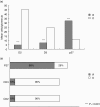
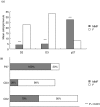
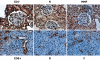
The response of mesangial cells to a phlogistic challenge includes cell proliferation and mesangial matrix expansion. Cell proliferation is a highly regulated process which includes enhancing factors such as cyclins, cyclin dependent kinases, and inhibitory proteins, such as p27(kip1). The aim of the study was to evaluate the effects of Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), and roscovitine (R), on the cell cycle regulatory system when administered in the florid phase of the experimental model of mesangial proliferative nephritis induced by the anti Thy-1 antigen monoclonal antibody. Three days after nephritis induction, different groups were given MMF and R. Rats treated with MMF or R showed a slight decrease in mesangial proliferation and matrix expansion. Samples of cortical tissue were tested by 'real time' RT-PCR in order to study gene expression of cyclins B, D1, D2, D3, E, and the cyclin inhibitor p27(kip1). Localization of mRNA was evaluated by in situ hybridization. Real time RT-PCR analysis showed a significant decrease in cyclins B, D1, D2, and D3 in rats treated with either MMF or R as compared to controls. Both MMF and R treatment induced a significant increase in p27(kip1) mRNA expression. In situ hybridization showed a mesangial-endothelial expression pattern in glomeruli. The number of labelled cells per glomerulus, the number of positive glomeruli in each examined slide as well as cyclin D2 and D3 signal intensity was significantly lower in rats treated with MMF or R as compared to controls, whereas MMF or R treatment up-regulated p27(kip1) mRNA expression. Immunohistochemical evaluation of p27(kip1) aimed to examine the influence of MMF or R on protein expression confirmed up-regulation.
Figures



References
-
- Ooi BS, Cohen DJ, Veis JH. Biology of the mesangial cell in glomerulonephritis- role of cytokines. Proc Soc Exp Biol Medical. 1996;213:230–7. - PubMed
-
- Couser WG. Pathogenesis of glomerular damage in glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998;13:10–5. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993;73:1059–65. - PubMed
-
- Weiberg RA. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell. 1995;81:323–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

