Generation of Th1 T cell responses directed to a HLA Class II restricted epitope from the Aspergillus f16 allergen
- PMID: 15654824
- PMCID: PMC1809287
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02699.x
Generation of Th1 T cell responses directed to a HLA Class II restricted epitope from the Aspergillus f16 allergen
Erratum in
- Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Apr;140(1):192-3
Abstract
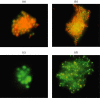
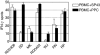
The Aspergillus allergen Asp f16 has been shown to confer protective Th1 T cell-mediated immunity against infection with Aspergillus conidia in murine models. Here, we use overlapping (11-aa overlap with preceding peptide) pentadecapeptides spanning the entire 427-aa coding region of Asp f16 presented on autologous dendritic cells (DC) to evaluate the ability of this antigen to induce Th1 responses in humans. Proliferative responses were induced in five out of five donors, and one line with a high frequency of interferon (IFN)-gamma-producing CD4(+) T cells in response to the complete peptide pool was characterized. This line was cytotoxic to autologous pool-pulsed and Aspergillus culture extract-pulsed targets. Limitation of cytotoxicity to the CD4(+) T cell subset was demonstrated by co-expression of the degranulation marker CD107a in response to peptide pool-pulsed targets. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) killed Aspergillus hyphae and CTL culture supernatant killed Aspergillus conidia. By screening 21 smaller pools and individual peptides shared by positive pools we identified a single candidate sequence of TWSIDGAVVRT that elicited responses equal to the complete pool. The defined epitope was presented by human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-DRB1-0301. These data identify the first known Aspergillus-specific T cell epitope and support the use of Asp f16 in clinical immunotherapy protocols to prime protective immune responses to prevent or treat Aspergillus infection in immunocompromised patients.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Adoptive immunity mediated by HLA-A*0201 restricted Asp f16 peptides-specific CD8+ T cells against Aspergillus fumigatus infection.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012 Nov;31(11):3089-96. doi: 10.1007/s10096-012-1670-2. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22696051
-
Stimulation by means of dendritic cells followed by Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cells as antigen-presenting cells is more efficient than dendritic cells alone in inducing Aspergillus f16-specific cytotoxic T cell responses.Clin Exp Immunol. 2008 Feb;151(2):284-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03544.x. Epub 2007 Nov 14. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18005260 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of cytotoxic T cell responses directed to human leucocyte antigen Class I restricted epitopes from the Aspergillus f16 allergen.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Apr;140(1):81-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02738.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15762878 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine progress.Med Mycol. 2009;47 Suppl 1:S394-400. doi: 10.1080/13693780802552614. Epub 2009 Feb 26. Med Mycol. 2009. PMID: 19247869 Review.
-
Cultivated anti-Aspergillus T(H)1 cells.Med Mycol. 2009;47 Suppl 1:S170-4. doi: 10.1080/13693780802169120. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Med Mycol. 2009. PMID: 18651313 Review.
Cited by
-
Adoptive immunity mediated by HLA-A*0201 restricted Asp f16 peptides-specific CD8+ T cells against Aspergillus fumigatus infection.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012 Nov;31(11):3089-96. doi: 10.1007/s10096-012-1670-2. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22696051
-
Prophylactic and Therapeutic Potential of Asp f1 Epitopes in Naïve and Sensitized BALB/c Mice.Immune Netw. 2009 Oct;9(5):179-91. doi: 10.4110/in.2009.9.5.179. Epub 2009 Oct 30. Immune Netw. 2009. PMID: 20157606 Free PMC article.
-
Healthy human T-Cell Responses to Aspergillus fumigatus antigens.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 17;5(2):e9036. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009036. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20174463 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy for opportunistic infections: Current status and future perspectives.Virulence. 2016 Nov 16;7(8):939-949. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1207038. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Virulence. 2016. PMID: 27385102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimulation by means of dendritic cells followed by Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cells as antigen-presenting cells is more efficient than dendritic cells alone in inducing Aspergillus f16-specific cytotoxic T cell responses.Clin Exp Immunol. 2008 Feb;151(2):284-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03544.x. Epub 2007 Nov 14. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18005260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wiederhold NP, Lewis RE, Kontoyiannis DP. Invasive aspergillosis in patients with hematologic malignancies. Pharmacotherapy. 2003;23:1592–610. - PubMed
-
- Denning DW. Invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:781–803. - PubMed
-
- Marr KA, Patterson T, Denning D. Aspergillosis. Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and therapy. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2002;16:875–94. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda T, Boeckh M, Carter RA, et al. Risks and outcomes of invasive fungal infections in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplants after nonmyeloablative conditioning. Blood. 2003;102:827–33. - PubMed
-
- Denning DW. Diagnosis and management of invasive aspergillosis. Curr Clin Top Infect Dis. 1996;16:277–99. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

