Deficiency of the mannan-binding lectin pathway of complement and poor outcome in cystic fibrosis: bacterial colonization may be decisive for a relationship
- PMID: 15654829
- PMCID: PMC1809291
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02690.x
Deficiency of the mannan-binding lectin pathway of complement and poor outcome in cystic fibrosis: bacterial colonization may be decisive for a relationship
Abstract
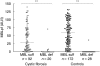
In cystic fibrosis (CF) prognosis concerning lung damage development is highly variable and difficult to predict. Mannan-binding lectin (MBL) deficiency has been reported to be associated with poor outcome in CF lung disease. MBL is a recognition molecule of the MBL pathway of the complement system and is encoded by a gene characterized by a high degree of polymorphism. Some genotypes result in low serum concentrations of MBL. MBL-associated serine protease 2 (MASP-2) is another protein belonging to the MBL pathway. A mutation resulting in low levels of MASP-2 in serum has been described recently. In the present study, 112 CF patients aged 4-54 years were investigated for MBL and MASP-2 genotypes, serum levels of MBL and MASP-2 and the MBL pathway function in serum. No correlation to reduced lung function or need for lung transplantation was seen, either for MBL deficiency, MASP-2 gene mutation or reduced MBL pathway function. However, in the 27 patients colonized with Staphylococcus aureus, MBL-deficient genotypes were associated with decreased lung function. As expected, MBL pathway function in serum was reduced both in MBL-deficient patients and in patients carrying a mutant MASP-2 allele. An unexpected finding was that CF patients had higher serum levels of MBL than healthy controls when corrected for MBL genotype. In conclusion, MBL pathway function was affected both by MBL and by MASP-2 genotypes. However, MBL or MASP-2 levels in serum did not affect the clinical outcome in the cohort of CF patients studied.
Figures



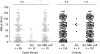
Similar articles
-
The mannan-binding lectin pathway and lung disease in cystic fibrosis--disfunction of mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease 2 (MASP-2) may be a major modifier.Clin Immunol. 2006 Dec;121(3):324-31. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2006.08.014. Epub 2006 Oct 12. Clin Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17045845
-
Polymorphisms in the lectin pathway genes as a possible cause of early chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonization in cystic fibrosis patients.Hum Immunol. 2012 Nov;73(11):1175-83. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2012.08.010. Epub 2012 Aug 29. Hum Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22940091
-
Mannose-binding lectin (MBL)-associated serine protease (MASP)-1 contributes to activation of the lectin complement pathway.J Immunol. 2008 May 1;180(9):6132-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.9.6132. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18424734
-
The mannan-binding lectin-associated serine proteases (MASPs) and MAp19: four components of the lectin pathway activation complex encoded by two genes.Immunobiology. 2002 Sep;205(4-5):455-66. doi: 10.1078/0171-2985-00146. Immunobiology. 2002. PMID: 12396007 Review.
-
Impact of mannose-binding lectin insufficiency on the course of cystic fibrosis: A review and meta-analysis.Glycobiology. 2011 Mar;21(3):271-82. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwq161. Epub 2010 Nov 2. Glycobiology. 2011. PMID: 21045008 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic influences on cystic fibrosis lung disease severity.Front Pharmacol. 2013 Apr 23;4:40. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2013.00040. eCollection 2013. Front Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23630497 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus adaptive evolution: Recent insights on how immune evasion, immunometabolic subversion and host genetics impact vaccine development.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Dec 27;12:1060810. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1060810. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36636720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mannose-binding lectin (MBL) as prognostic factor in paediatric oncology patients.Clin Exp Immunol. 2011 Jul;165(1):51-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04398.x. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21488869 Free PMC article.
-
Update on gene modifiers in cystic fibrosis.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2008 Nov;14(6):559-66. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e3283121cdc. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2008. PMID: 18812833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MBL-associated serine proteases (MASPs) and infectious diseases.Mol Immunol. 2015 Sep;67(1):85-100. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.03.245. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25862418 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Riordan JR, Rommens JM, Kerem B, et al. Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: cloning and characterization of complementary DNA. Science. 1989;245:1066–73. - PubMed
-
- Lannefors L, Lindgren A. Demographic transition of the Swedish cystic fibrosis community − results of modern care. Respir Med. 2002;96:681–5. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 1994 Annual data report. Bethesda, MD: Cystic Fibrosis Foundation; 1995. Patient registry.
-
- Rowntree RK, Harris A. The phenotypic consequences of CFTR mutations. Ann Hum Genet. 2003;67:471–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

