Excessive expression of Txk, a member of the Tec family of tyrosine kinases, contributes to excessive Th1 cytokine production by T lymphocytes in patients with Behcet's disease
- PMID: 15654836
- PMCID: PMC1809281
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02688.x
Excessive expression of Txk, a member of the Tec family of tyrosine kinases, contributes to excessive Th1 cytokine production by T lymphocytes in patients with Behcet's disease
Abstract
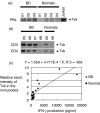
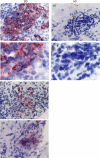
Excessive Th1 cell function is importantly involved in the pathogenesis of Behcet's disease (BD). We previously found that Txk, a member of the Tec family of tyrosine kinases, acts as a Th1 cell specific transcription factor. To investigate immune aberration in the pathogenesis of BD, we studied the expression of Txk and Th1 cytokines in peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) and skin lesions in patients with BD. Cytokine production by the lymphocytes was assessed using ELISA. PBL produced excessive Th1 associated cytokines including IFN-gamma and IL-12 spontaneously and in response to exogenous HSP60-derived peptide stimulation, which was shown to induce proliferation of PBL, in patients with BD. Circulating CD4+ T cells expressed excessive Txk protein. A majority of cells infiltrating into skin lesions expressed IFN-gamma in the BD specimens. IL-12 and IL-18 were also expressed in the mononuclear cell aggregates. Lymphocytes accumulating in the skin lesion expressed higher levels of Txk as compared with atopic dermatitis lesions, a typical Th2 disease. IFN-gamma, IL-18 and Il-12 were detected in the BD skin lesions, which may induce preferential development of Th1 cells in patients with BD. The mononuclear cell aggregates contained Txk expressing cells in such skin lesions. Collectively, Txk expressing Th1 cells and the Th1 associated cytokines may play a critical role in the development of skin lesions in BD.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Skewed Th1 responses caused by excessive expression of Txk, a member of the Tec family of tyrosine kinases, in patients with Behcet's disease.Clin Med Res. 2006 Jun;4(2):147-51. doi: 10.3121/cmr.4.2.147. Clin Med Res. 2006. PMID: 16809408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Th1-dominant shift of T cell cytokine production, and subsequent reduction of serum immunoglobulin E response by administration in vivo of plasmid expressing Txk/Rlk, a member of Tec family tyrosine kinases, in a mouse model.Clin Exp Allergy. 2004 Jun;34(6):965-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.01981.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004. PMID: 15196287
-
Involvement of Th1 cells and heat shock protein 60 in the pathogenesis of intestinal Behcet's disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Feb;139(2):371-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02695.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15654837 Free PMC article.
-
Increased entry of CD4+ T cells into the Th1 cytokine effector pathway during T-cell division following stimulation in Behcet's disease.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004 Jul;43(7):843-51. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh195. Epub 2004 May 18. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2004. PMID: 15150429
-
Role of Txk, a member of the Tec family of tyrosine kinases, in immune-inflammatory diseases.Int Rev Immunol. 2007 Sep-Dec;26(5-6):333-48. doi: 10.1080/08830180701690835. Int Rev Immunol. 2007. PMID: 18027204 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathogenesis of Behçet's disease: autoinflammatory features and beyond.Semin Immunopathol. 2015 Jul;37(4):413-8. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0502-8. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Semin Immunopathol. 2015. PMID: 26068404 Review.
-
HSP60 and anti-HSP60 antibodies in vasculitis: they are two of a kind.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008 Oct;35(1-2):66-71. doi: 10.1007/s12016-007-8062-x. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18188708 Review.
-
Immunopathogenic Role of Herpes Simplex Virus in Behçet's Disease.Genet Res Int. 2013;2013:638273. doi: 10.1155/2013/638273. Epub 2013 Nov 24. Genet Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24349789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial DNA 3243 mutation may be associated with positivity of zinc transporter 8 autoantibody in cases of slowly progressive type 1 diabetes mellitus.Diabetol Int. 2024 Nov 21;16(1):188-193. doi: 10.1007/s13340-024-00776-9. eCollection 2025 Jan. Diabetol Int. 2024. PMID: 39877436
-
Excessive CD4+ T cells co-expressing interleukin-17 and interferon-γ in patients with Behçet's disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2012 Apr;168(1):68-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04543.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22385240 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behcet's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1284–91. - PubMed
-
- Lee EB, Kim JY, Lee YJ, Park MH, Song YW. TNF and TNF receptor polymorphisms in Korean Behcet's disease patients. Hum Immunol. 2003;64:614–20. - PubMed
-
- Gul A, Hajeer AH, Worthington J, Ollier WE, Silman AJ. Linkage mapping of a novel susceptibility locus for Behcet's disease to chromosome 6p22–23. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:2693–6. - PubMed
-
- Kotter I, Gunaydin I, Stubiger N, et al. Comparative analysis of the association of HLA-B*51 suballeles with Behcet's disease in patients of German and Turkish origin. Tissue Antigens. 2001;58:166–70. - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Bang D, Cho YH, Lee ES, Sohn S. Polymerase chain reaction reveals herpes simplex virus DNA in saliva of patients with Behcet's disease. Arch Dermatol Res. 1996;288:179–83. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

