Gastrin promotes human colon cancer cell growth via CCK-2 receptor-mediated cyclooxygenase-2 induction and prostaglandin E2 production
- PMID: 15655524
- PMCID: PMC1576011
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706053
Gastrin promotes human colon cancer cell growth via CCK-2 receptor-mediated cyclooxygenase-2 induction and prostaglandin E2 production
Abstract
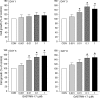
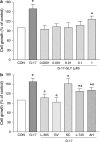
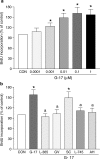
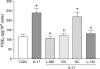
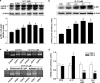
The present study investigates the effects of gastrin-17 on human colon cancer HT-29 cells to examine whether gastrin receptor (CCK-2), cyclooxygenase (COX-1, COX-2) isoforms and prostaglandin receptor pathways interact to control cell growth. Reverse transcription (RT)-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis demonstrated that HT-29 cells are endowed with the naive expression of CCK-2 receptor (short splice variant), COX-1, COX-2 and prostaglandin EP(4) receptor, but not gastrin. Gastrin-17 significantly promoted cell growth and DNA synthesis. Both these stimulating effects were abolished by L-365,260 or GV150013 (CCK-2 receptor antagonists), but were unaffected by SC-560 (COX-1 inhibitor). L-745,337 (COX-2 inhibitor) or AH-23848B (EP(4) receptor antagonist) partly reversed gastrin-17-induced cell growth, while they fully antagonized the enhancing action on DNA synthesis. HT-29 cells responded to gastrin-17 with a significant increase in prostaglandin E(2) release. This enhancing effect was completely counteracted by L-365,260, GV150013 or L-745,337, while it was insensitive to cell incubation with SC-560. Exposure of HT-29 cells to gastrin-17 was followed by an increased phosphorylation of both extracellular regulated kinases (ERK-1/ERK-2) and Akt. Moreover, gastrin-17 enhanced the transcriptional activity of COX-2 gene promoter and stimulated COX-2 expression. These latter effects were antagonized by L-365,260 or GV150013, and could be blocked also by PD98059 (inhibitor of ERK-1/ERK-2 phosphorylation) or wortmannin (inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase). Analogously, gastrin-17-induced prostaglandin E(2) release was prevented by PD98059 or wortmannin. The present results suggest that (a) in human colon cancer cells endowed with CCK-2 receptors, gastrin-17 is able to enhance the transcriptional activity of COX-2 gene through the activation of ERK-1/ERK-2- and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathways; (b) these stimulant actions lead to downstream increments of COX-2 expression, followed by prostaglandin E(2) production and EP(4) receptor activation; (c) the recruitment of COX-2/prostaglandin pathways contributes to the growth-promoting actions exerted by gastrin-17.
Figures




References
-
- BELLEY A., CHADEE K. Prostaglandin E2 stimulates rat and human colonic mucin exocytosis via the EP4 receptor. Gastroenterology. 1999;117:1352–1362. - PubMed
-
- DI POPOLO A., MEMOLI A., APICELLA A., TUCCILLO C., DI PALMA A., RICCHI P., ACQUAVIVA A.M., ZARRILLI R. IGF-II/IGF-I receptor pathway up-regulates COX-2 mRNA expression and PGE2 synthesis in Caco-2 human colon carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2000;19:5517–5524. - PubMed
-
- DOCKRAY G.J., VARRO A., DIMALINE R., WANG T. The gastrins: their production and biological activities. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001;63:119–139. - PubMed
-
- DU BOIS R.N., ABRAMSON S.B., CROFFORD L., GUPTA R.A., SIMON L.S., VAN DE PUTTE L.B., LIPSKY P.E. Cyclooxygenase in biology and disease. FASEB J. 1998;12:1063–1073. - PubMed
-
- GUO Y.-S., CHENG J.-Z., JIN G.-F., GUTKIND J.S., HELLMICH M.R., TOWNSEND M.T. Gastrin stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 expression in intestinal epithelial cells through multiple signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:48755–48763. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

