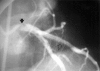
Spontaneous dissection of native coronary arteries
- PMID: 15657239
- PMCID: PMC1768706
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2003.014423
Spontaneous dissection of native coronary arteries
Figures
References
-
- Tsimikas S, Giodano F, Tarazi R, et al. Spontaneous coronary artery dissection in patients with renal transplantation. J Invas Cardiol 1999;11:316–21. - PubMed
-
- DeMaio S, Kinsella S, Silverman M. Clinical course and long term prognosis of spontaneous coronary artery dissection. Am Heart J 1989;64:471–4. - PubMed
-
- Parry R, MacConnell T, Wilde P. Case report: spontaneous coronary artery dissection. Clin Radiol 1994;49:142–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources