Prevention of UV radiation-induced immunosuppression by IL-12 is dependent on DNA repair
- PMID: 15657287
- PMCID: PMC2212783
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20041212
Prevention of UV radiation-induced immunosuppression by IL-12 is dependent on DNA repair
Abstract
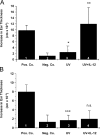
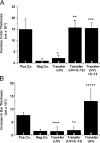
The immunostimulatory cytokine IL-12 is able to antagonize immunosuppression induced by solar/ultraviolet (UV) radiation via yet unknown mechanisms. IL-12 was recently found to induce deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) repair. UV-induced DNA damage is an important molecular trigger for UV-mediated immunosuppression. Thus, we initiated studies into immune restoration by IL-12 to discern whether its effects are linked to DNA repair. IL-12 prevented both UV-induced suppression of the induction of contact hypersensitivity and the depletion of Langerhans cells, the primary APC of the skin, in wild-type but not in DNA repair-deficient mice. IL-12 did not prevent the development of UV-induced regulatory T cells in DNA repair-deficient mice. In contrast, IL-12 was able to break established UV-induced tolerance and inhibited the activity of regulatory T cells independent of DNA repair. These data identify a new mechanism by which IL-12 can restore immune responses and also demonstrate a link between DNA repair and the prevention of UV-induced immunosuppression by IL-12.
Figures



References
-
- Fisher, G.J., S.C. Datta, H.S. Halwar, Z.Q. Wang, J. Varani, S. Kang, and J.J. Voorhees. 1996. Molecular basis of sun-induced premature skin ageing and retinoid antagonism. Nature. 379:335–339. - PubMed
-
- de Gruijl, F.R., H.J. Sterenborg, P.D. Forbes, R.E. Davies, C. Cole, G. Kelfkens, H. van Weelden, H. Slaper, and J.C. van der Leun. 1993. Wavelength dependence of skin cancer induction by ultraviolet irradiation of albino hairless mice. Cancer Res. 53:53–60. - PubMed
-
- Chapman, R.S., K.D. Cooper, E.C. DeFabo, J.E. Frederick, K.N. Gelatt, S.P. Hammond, P. Hersey, H.S. Koren, R.D. Ley, F. Noonan, et al. 1995. Solar ultraviolet radiation and the risk of infectious disease. Photochem. Photobiol. 61:223–247. - PubMed
-
- Toews, G.B., P.R. Bergstresser, and J.W. Streilein. 1980. Epidermal Langerhans cell density determines whether contact hypersensitivity or unresponsiveness follows skin painting with DNFB. J. Immunol. 124:445–453. - PubMed
-
- Cooper, K.D., L. Oberhelman, T.A. Hamilton, O. Baadsgaard, M. Terhune, G. LeVee, T. Anderson, and H. Koren. 1992. UV exposure reduces immunization rates and promotes tolerance to epicutaneous antigens in humans: Relationship to dose, CD1a-DR+epidermal macrophage induction, and Langerhans cell depletion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 89:8497–8501. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

