Actin-myosin-based contraction is responsible for apoptotic nuclear disintegration
- PMID: 15657395
- PMCID: PMC2171584
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200409049
Actin-myosin-based contraction is responsible for apoptotic nuclear disintegration
Abstract
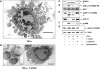
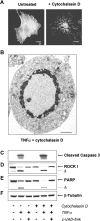
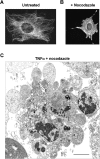
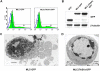
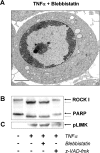
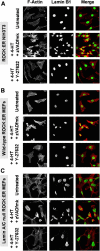
Membrane blebbing during the apoptotic execution phase results from caspase-mediated cleavage and activation of ROCK I. Here, we show that ROCK activity, myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation, MLC ATPase activity, and an intact actin cytoskeleton, but not microtubular cytoskeleton, are required for disruption of nuclear integrity during apoptosis. Inhibition of ROCK or MLC ATPase activity, which protect apoptotic nuclear integrity, does not affect caspase-mediated degradation of nuclear proteins such as lamins A, B1, or C. The conditional activation of ROCK I was sufficient to tear apart nuclei in lamin A/C null fibroblasts, but not in wild-type fibroblasts. Thus, apoptotic nuclear disintegration requires actin-myosin contractile force and lamin proteolysis, making apoptosis analogous to, but distinct from, mitosis where nuclear disintegration results from microtubule-based forces and from lamin phosphorylation and depolymerization.
Figures



References
-
- Apel, E.D., R.M. Lewis, R.M. Grady, and J.R. Sanes. 2000. Syne-1, a dystrophin- and Klarsicht-related protein associated with synaptic nuclei at the neuromuscular junction. J. Biol. Chem. 275:31986–31995. - PubMed
-
- Beaudouin, J., D. Gerlich, N. Daigle, R. Eils, and J. Ellenberg. 2002. Nuclear envelope breakdown proceeds by microtubule-induced tearing of the lamina. Cell. 108:83–96. - PubMed
-
- Broers, J.L., N.M. Bronnenberg, H.J. Kuijpers, B. Schutte, C.J. Hutchison, and F.C. Ramaekers. 2002. Partial cleavage of A-type lamins concurs with their total disintegration from the nuclear lamina during apoptosis. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 81:677–691. - PubMed
-
- Bubb, M.R., I. Spector, A.D. Bershadsky, and E.D. Korn. 1995. Swinholide A is a microfilament disrupting marine toxin that stabilizes actin dimers and severs actin filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 270:3463–3466. - PubMed

