RAD51-dependent break-induced replication differs in kinetics and checkpoint responses from RAD51-mediated gene conversion
- PMID: 15657422
- PMCID: PMC544012
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.933-944.2005
RAD51-dependent break-induced replication differs in kinetics and checkpoint responses from RAD51-mediated gene conversion
Abstract
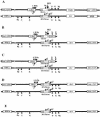
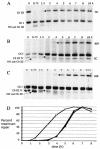
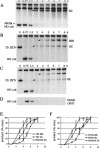
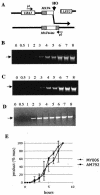
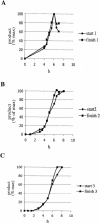
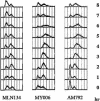
Diploid Saccharomyces cells experiencing a double-strand break (DSB) on one homologous chromosome repair the break by RAD51-mediated gene conversion >98% of the time. However, when extensive homologous sequences are restricted to one side of the DSB, repair can occur by both RAD51-dependent and RAD51-independent break-induced replication (BIR) mechanisms. Here we characterize the kinetics and checkpoint dependence of RAD51-dependent BIR when the DSB is created within a chromosome. Gene conversion products appear within 2 h, and there is little, if any, induction of the DNA damage checkpoint; however, RAD51-dependent BIR occurs with a further delay of 2 to 4 h and cells arrest in response to the G(2)/M DNA damage checkpoint. RAD51-dependent BIR does not require special facilitating sequences that are required for a less efficient RAD51-independent process. RAD51-dependent BIR occurs efficiently in G(2)-arrested cells. Once repair is initiated, the rate of repair replication during BIR is comparable to that of normal DNA replication, as copying of >100 kb is completed less than 30 min after repair DNA synthesis is detected close to the DSB.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
