Silencing of unpaired chromatin and histone H2A ubiquitination in mammalian meiosis
- PMID: 15657431
- PMCID: PMC543997
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.1041-1053.2005
Silencing of unpaired chromatin and histone H2A ubiquitination in mammalian meiosis
Abstract
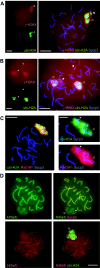
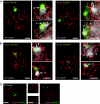
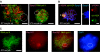
During meiotic prophase in male mammals, the X and Y chromosomes are incorporated in the XY body. This heterochromatic body is transcriptionally silenced and marked by increased ubiquitination of histone H2A. This led us to investigate the relationship between histone H2A ubiquitination and chromatin silencing in more detail. First, we found that ubiquitinated H2A also marks the silenced X chromosome of the Barr body in female somatic cells. Next, we studied a possible relationship between H2A ubiquitination, chromatin silencing, and unpaired chromatin in meiotic prophase. The mouse models used carry an unpaired autosomal region in male meiosis or unpaired X and Y chromosomes in female meiosis. We show that ubiquitinated histone H2A is associated with transcriptional silencing of large chromatin regions. This silencing in mammalian meiotic prophase cells concerns unpaired chromatin regions and resembles a phenomenon described for the fungus Neurospora crassa and named meiotic silencing by unpaired DNA.
Figures



References
-
- Baarends, W. M., J. W. Hoogerbrugge, H. P. Roest, M. Ooms, J. Vreeburg, J. H. J. Hoeijmakers, and J. A. Grootegoed. 1999. Histone ubiquitination and chromatin remodeling in mouse spermatogenesis. Dev. Biol. 207:322-333. - PubMed
-
- Bailly, V., J. Lamb, P. Sung, S. Prakash, and L. Prakash. 1994. Specific complex formation between yeast RAD6 and RAD18 proteins: a potential mechanism for targeting RAD6 ubiquitin-conjugating activity to DNA damage sites. Genes Dev. 8:811-820. - PubMed
-
- Barr, M. L., and E. G. Bertram. 1949. A morphological distinction between neurones of the male and female, and the behaviour of the nucleolar satellite during accelerated nucleoprotein synthesis. Nature 163:676-677. - PubMed
-
- Briggs, S. D., T. Xiao, Z. W. Sun, J. A. Caldwell, J. Shabanowitz, D. F. Hunt, C. D. Allis, and B. D. Strahl. 2002. Gene silencing: trans-histone regulatory pathway in chromatin. Nature 418:498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
