Phosphorylation of Par-4 by protein kinase A is critical for apoptosis
- PMID: 15657440
- PMCID: PMC544017
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.1146-1161.2005
Phosphorylation of Par-4 by protein kinase A is critical for apoptosis
Abstract
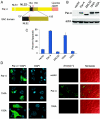
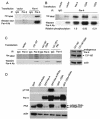
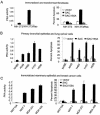
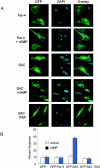
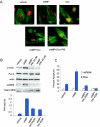
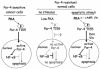
Despite distinct dissimilarities, diverse cancers express several common protumorigenic traits. We present here evidence that the proapoptotic protein Par-4 utilizes one such common tumorigenic trait to become selectively activated and induce apoptosis in cancer cells. Elevated protein kinase A (PKA) activity noted in cancer cells activated the apoptotic function of ectopic Par-4 or its SAC (selective for apoptosis induction in cancer cells) domain, which induces apoptosis selectively in cancer cells and not in normal or immortalized cells. PKA preferentially phosphorylated Par-4 at the T155 residue within the SAC domain in cancer cells. Moreover, pharmacological-, peptide-, or small interfering RNA-mediated inhibition of PKA activity in cancer cells resulted in abrogation of both T155 phosphorylation and apoptosis by Par-4. The mechanism of activation of endogenous Par-4 was similar to that of ectopic Par-4, and in response to exogenous stimuli, endogenous Par-4 induced apoptosis by a PKA- and phosphorylated T155-dependent mechanism. Enforced elevation of PKA activity in normal cells resulted in apoptosis by the SAC domain of Par-4 in a T155-dependent manner. Together, these observations suggest that selective apoptosis of cancer cells by the SAC domain of Par-4 involves phosphorylation of T155 by PKA. These findings uncover a novel mechanism engaging PKA, a procancerous activity commonly elevated in most tumor cells, to activate the cancer selective apoptotic action of Par-4.
Figures





References
-
- Boehrer, S., K. U. Chow, E. Puccetti, M. Ruthardt, S. Godzisard, A. Krapohl, B. Schneider, D. Hoelzer, P. S. Mitrou, V. M. Rangnekar, and E. Weidmann. 2001. Deregulated expression of prostate apoptosis response gene-4 in less differentiated lymphocytes and inverse expressional patterns of par-4 and bcl-2 in acute lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol. J. 2:103-107. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty, M., S. G. Qiu, K. M. Vasudevan, and V. M. Rangnekar. 2001. Par-4 drives trafficking and activation of Fas and Fasl to induce prostate cancer cell apoptosis and tumor regression. Cancer Res. 61:7255-7263. - PubMed
-
- Cho, Y. S., Y. G. Park, Y. N. Lee, M. K. Kim, S. Bates, L. Tan, and Y. S. Cho-Chung. 2000. Extracellular protein kinase A as a cancer biomarker: its expression by tumor cells and reversal by a myristate-lacking Cα and RIIβ subunit overexpression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:835-840. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cho-Chung, Y. S., M. Nesterova, K. G. Becker, R. Srivastava, Y. G. Park, Y. N. Lee, Y. S. Cho, M. K. Kim, C. Neary, and C. Cheadle. 2002. Dissecting the circuitry of protein kinase A and cAMP signaling in cancer genesis: antisense, microarray, gene overexpression, and transcription factor decoy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 968:22-36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
