A direct intersection between p53 and transforming growth factor beta pathways targets chromatin modification and transcription repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene
- PMID: 15657445
- PMCID: PMC544019
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.1200-1212.2005
A direct intersection between p53 and transforming growth factor beta pathways targets chromatin modification and transcription repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene
Abstract
We purified the oncoprotein SnoN and found that it functions as a corepressor of the tumor suppressor p53 in the regulation of the hepatic alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) tumor marker gene. p53 promotes SnoN and histone deacetylase interaction at an overlapping Smad binding, p53 regulatory element (SBE/p53RE) in AFP. Comparison of wild-type and p53-null mouse liver tissue by using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) reveals that the absence of p53 protein correlates with the disappearance of SnoN at the SBE/p53RE and loss of AFP developmental repression. Treatment of AFP-expressing hepatoma cells with transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) induced SnoN transcription and Smad2 activation, concomitant with AFP repression. ChIP assays show that TGF-beta1 stimulates p53, Smad4, P-Smad2 binding, and histone H3K9 deacetylation and methylation, at the SBE/p53RE. Depletion, by small interfering RNA, of SnoN and/or p53 in hepatoma cells disrupted repression of AFP transcription. These findings support a model of cooperativity between p53 and TGF-beta effectors in chromatin modification and transcription repression of an oncodevelopmental tumor marker gene.
Figures

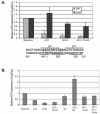
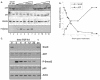
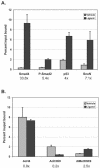
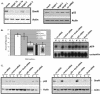
Similar articles
-
Chromatin-bound p53 anchors activated Smads and the mSin3A corepressor to confer transforming-growth-factor-beta-mediated transcription repression.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Mar;28(6):1988-98. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01442-07. Epub 2008 Jan 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18212064 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor interactions and chromatin modifications associated with p53-mediated, developmental repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Mar;25(6):2147-57. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.6.2147-2157.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15743813 Free PMC article.
-
Family members p53 and p73 act together in chromatin modification and direct repression of alpha-fetoprotein transcription.J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 25;280(47):39152-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504655200. Epub 2005 Oct 2. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16203738
-
[Ski and SnoN: antagonistic proteins of TGFbeta signaling].Bull Cancer. 2000 Feb;87(2):135-7. Bull Cancer. 2000. PMID: 10705283 Review. French.
-
SnoN in mammalian development, function and diseases.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Dec;10(6):670-5. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2010.08.006. Epub 2010 Sep 6. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20822955 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of p53 activation and physiological relevance in the developing kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Apr 15;302(8):F928-40. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00642.2011. Epub 2012 Jan 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22237799 Free PMC article.
-
Convergence of p53 and transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) signaling on activating expression of the tumor suppressor gene maspin in mammary epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 23;282(8):5661-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608499200. Epub 2007 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17204482 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of SnoN gene silencing by siRNA on the cell proliferation and apoptosis of human pancreatic cancer cells.Diagn Pathol. 2015 Apr 18;10:30. doi: 10.1186/s13000-015-0267-3. Diagn Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25907906 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β/SMAD Target gene SKIL is negatively regulated by the transcriptional cofactor complex SNON-SMAD4.J Biol Chem. 2012 Aug 3;287(32):26764-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.386599. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22674574 Free PMC article.
-
Scutellarin Enhances Antitumor Effects and Attenuates the Toxicity of Bleomycin in H22 Ascites Tumor-Bearing Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jun 14;9:615. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00615. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29962947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyoshi, S., H. Inoue, J. Hanai, K. Kusanagi, N. Nemoto, K. Miyazono, and M. Kawabata. 1999. c-Ski acts as a transcriptional co-repressor in transforming growth factor-beta signaling through interaction with smads. J. Biol. Chem. 274:35269-35277. - PubMed
-
- Andrisani, O. M., and S. Barnabas. 1999. The transcriptional function of the hepatitis B virus X protein and its role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Oncol. 15:373-379. - PubMed
-
- Attisano, L. 2000. Smads as transcriptional co-modulators. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12:235-243. - PubMed
-
- Bargonetti, J., and J. J. Manfredi. 2002. Multiple roles of the tumor suppressor p53. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 14:86-91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
