A direct intersection between p53 and transforming growth factor beta pathways targets chromatin modification and transcription repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene
- PMID: 15657445
- PMCID: PMC544019
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.1200-1212.2005
A direct intersection between p53 and transforming growth factor beta pathways targets chromatin modification and transcription repression of the alpha-fetoprotein gene
Abstract
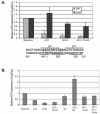
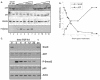
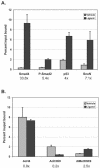
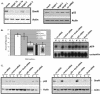
We purified the oncoprotein SnoN and found that it functions as a corepressor of the tumor suppressor p53 in the regulation of the hepatic alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) tumor marker gene. p53 promotes SnoN and histone deacetylase interaction at an overlapping Smad binding, p53 regulatory element (SBE/p53RE) in AFP. Comparison of wild-type and p53-null mouse liver tissue by using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) reveals that the absence of p53 protein correlates with the disappearance of SnoN at the SBE/p53RE and loss of AFP developmental repression. Treatment of AFP-expressing hepatoma cells with transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) induced SnoN transcription and Smad2 activation, concomitant with AFP repression. ChIP assays show that TGF-beta1 stimulates p53, Smad4, P-Smad2 binding, and histone H3K9 deacetylation and methylation, at the SBE/p53RE. Depletion, by small interfering RNA, of SnoN and/or p53 in hepatoma cells disrupted repression of AFP transcription. These findings support a model of cooperativity between p53 and TGF-beta effectors in chromatin modification and transcription repression of an oncodevelopmental tumor marker gene.
Figures

References
-
- Akiyoshi, S., H. Inoue, J. Hanai, K. Kusanagi, N. Nemoto, K. Miyazono, and M. Kawabata. 1999. c-Ski acts as a transcriptional co-repressor in transforming growth factor-beta signaling through interaction with smads. J. Biol. Chem. 274:35269-35277. - PubMed
-
- Andrisani, O. M., and S. Barnabas. 1999. The transcriptional function of the hepatitis B virus X protein and its role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Int. J. Oncol. 15:373-379. - PubMed
-
- Attisano, L. 2000. Smads as transcriptional co-modulators. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12:235-243. - PubMed
-
- Bargonetti, J., and J. J. Manfredi. 2002. Multiple roles of the tumor suppressor p53. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 14:86-91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
