Polymorphisms in the tyrosine kinase 2 and interferon regulatory factor 5 genes are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 15657875
- PMCID: PMC1196404
- DOI: 10.1086/428480
Polymorphisms in the tyrosine kinase 2 and interferon regulatory factor 5 genes are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
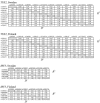
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex systemic autoimmune disease caused by both genetic and environmental factors. Genome scans in families with SLE point to multiple potential chromosomal regions that harbor SLE susceptibility genes, and association studies in different populations have suggested several susceptibility alleles for SLE. Increased production of type I interferon (IFN) and expression of IFN-inducible genes is commonly observed in SLE and may be pivotal in the molecular pathogenesis of the disease. We analyzed 44 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 13 genes from the type I IFN pathway in 679 Swedish, Finnish, and Icelandic patients with SLE, in 798 unaffected family members, and in 438 unrelated control individuals for joint linkage and association with SLE. In two of the genes--the tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) and IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) genes--we identified SNPs that displayed strong signals in joint analysis of linkage and association (unadjusted P<10(-7)) with SLE. TYK2 binds to the type I IFN receptor complex and IRF5 is a regulator of type I IFN gene expression. Thus, our results support a disease mechanism in SLE that involves key components of the type I IFN system.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- CHIP Bioinformatics Tools, http://snpper.chip.org/bio/top (for SNPer)
-
- dbSNP Home Page, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/
-
- Haploview, http://www.broad.mit.edu/mpg/haploview/
-
- Jost Web site, http://www.loujost.com/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for SLE) - PubMed
References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K (2004) Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4:499–511 - PubMed
-
- Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Karypis G, Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ, Shark KB, Grande WJ, Hughes KM, Kapur V, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW (2003) Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2610–2615 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnes B, Lubyova B, Pitha PM (2002) On the role of IRF in host defense. J Interferon Cytokine Res 22:59–71 - PubMed
-
- Barnes BJ, Kellum MJ, Pinder KE, Frisancho JA, Pitha PM (2003) Interferon regulatory factor 5, a novel mediator of cell cycle arrest and cell death. Cancer Res 63:6424–6431 - PubMed
-
- Barnes BJ, Moore PA, Pitha PM (2001) Virus-specific activation of a novel interferon regulatory factor, IRF-5, results in the induction of distinct interferon α genes. J Biol Chem 276:23382–23390 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

