Early and late HHV-6 gene transcripts in multiple sclerosis lesions and normal appearing white matter
- PMID: 15659422
- PMCID: PMC7109784
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awh390
Early and late HHV-6 gene transcripts in multiple sclerosis lesions and normal appearing white matter
Abstract
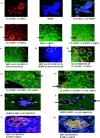
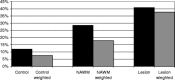
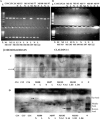
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the CNS, the aetiology of which is believed to have both genetic and environmental components. We have investigated one of the candidate viruses for the environmental component of multiple sclerosis, the neurotropic human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6). Utilizing fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) techniques, we have examined human post-mortem tissues for the presence of immediate early and late viral gene expression in multiple sclerosis patient normal appearing white matter (NAWM), lesional tissue and normal control brain samples. HHV-6 gene transcription was detected in all tissue samples and was restricted to oligodendrocytes, as determined by double mRNA FISH analysis. Quantitative analysis of viral mRNA expression indicated that both NAWM and lesional multiple sclerosis samples exhibited significantly higher levels of HHV-6 expression compared with the normal control samples. Lesional samples exhibited the highest levels of viral gene expression, with NAWM exhibiting an intermediate level between lesional and control tissues. Immunofluorescence against early and late HHV-6 proteins verified active translation of HHV-6 viral mRNA in oligodendrocytes. Southern blot analysis of nested polymerase chain reactions using extracted genomic DNA and cDNA confirmed the presence of the HHV-6 genome in all individuals, with the active expression profile mirroring the FISH results. The frequent high level of HHV-6 infection in multiple sclerosis samples suggests a possible role in pathogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Ablashi DV, Balanchandran N, Josephs SF, Hung CL, Krueger GR, Kramarsky B, et al. Genomic polymorphism, growth properties and immunologic variations in human herpesvirus-6 isolates. Virology 1991; 184: 545–52. - PubMed
-
- Ablashi DV, Lapps W, Kaplan M, Whitman JE, Richert JR, Pearson GR. Human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) infection in multiple sclerosis: a preliminary report. Mult Scler 1998; 4: 490–6. - PubMed
-
- Ablashi DV, Eastman HB, Owen CB, Roman MM, Friedman J, Zabriskie JB, et al. Frequent HHV-6 reactivation in multiple sclerosis (MS) and chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) patients. J Clin Virol 2000; 16: 179–91. - PubMed
-
- Akhyani N, Berti R, Brennan MB, Soldan SS, Eaton JM, McFarland, et al. Tissue distribution and variant characterization of human herpesvirus (HHV)-6: increased prevalence of HHV-6A in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Infect Dis 2000; 182: 1321–25. - PubMed
-
- Albright AV, Lavi E, Black JB, Goldberg S, O'Connor MJ, Gonzalez-Scarano F. The effect of human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) on cultured human neural cells: oligodendrocytes and microglia. J Neurovirol 1998; 4: 486–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

