Membrane receptors involved in modulation of responses of spinal dorsal horn interneurons evoked by feline group II muscle afferents
- PMID: 15659594
- PMCID: PMC1890036
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3797-04.2005
Membrane receptors involved in modulation of responses of spinal dorsal horn interneurons evoked by feline group II muscle afferents
Abstract
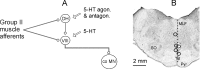
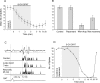
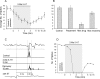
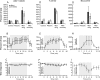
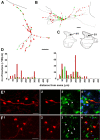
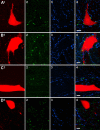
Modulatory actions of a metabotropic 5-HT1A&7 membrane receptor agonist and antagonist [(+/-)-8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin; N-[2-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-N-(2-pyridinyl) cyclohexane-carboxamide] and an ionotropic 5-HT3 membrane receptor agonist and antagonist [2-methyl-serotonin (2-Me 5-HT); N-(1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl)-6-chloro-4-methyl-3-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzoxazine-8-carboxamide hydrochloride] were investigated on dorsal horn interneurons mediating reflex actions of group II muscle afferents. All drugs were applied ionophoretically in deeply anesthetized cats. Effects of agonists were tested on extracellularly recorded responses of individual interneurons evoked by electrical stimulation of group II afferents in a muscle nerve. Effects of antagonists were tested against the depression of these responses after stimulation of raphe nuclei. The results show that both 5-HT1A&7 and 5-HT3 membrane receptors are involved in counteracting the activation of dorsal horn interneurons by group II afferents. Because only quantitative differences were found within the sample of the tested neurons, these results suggest that modulatory actions of 5-HT on excitatory and inhibitory interneurons might be similar. The relationship between 5-HT axons and axons immunoreactive for the 5-HT3A receptor subunit, which contact dorsal horn interneurons, was analyzed using immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy. Contacts from both types of axons were found on all interneurons, but their distribution and density varied, and there was no obvious relationship between them. In two of six interneurons, 5-HT3A-immunoreactive axons formed ring-like arrangements around the cell bodies. In previous studies, axons possessing 5-HT3 receptors were found to be excitatory, and as 2-Me 5-HT depressed transmission to dorsal horn interneurons, the results indicate that 5-HT operates at 5-HT3 receptors presynaptic to these neurons to depress excitatory transmission.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modulation of afferent-evoked neurotransmission by 5-HT3 receptors in young rat dorsal horn neurones in vitro: a putative mechanism of 5-HT3 induced anti-nociception.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Jun;127(4):843-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702592. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10433490 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors control the firing of serotoninergic neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the mouse: studies in 5-HT1B knock-out mice.Eur J Neurosci. 1999 Nov;11(11):3823-31. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00800.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10583471
-
Effects of monoamines on interneurons in four spinal reflex pathways from group I and/or group II muscle afferents.Eur J Neurosci. 2000 Feb;12(2):701-14. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00955.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10712650
-
5-hydroxytryptamine in migraine: The puzzling role of ionotropic 5-HT3 receptor in the context of established therapeutic effect of metabotropic 5-HT1 subtypes.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;179(3):400-415. doi: 10.1111/bph.15710. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34643938 Review.
-
[Serotonin receptor 1A-modulated dephosphorylation of glycine receptor α3: a new molecular mechanism of breathing control for compensation of opioid-induced respiratory depression without loss of analgesia].Schmerz. 2011 Jun;25(3):272-81. doi: 10.1007/s00482-011-1044-1. Schmerz. 2011. PMID: 21499860 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Challenges and Efficacy of Astrocyte-to-Neuron Reprogramming in Spinal Cord Injury: In Vitro Insights and In Vivo Outcomes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 21:2024.03.25.586619. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.25.586619. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 38585866 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Bioactive Six-Membered Heterocycles and Their Fused Analogues.Molecules. 2016 Apr 14;21(4):492. doi: 10.3390/molecules21040492. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27089315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Firing characteristics of deep dorsal horn neurons after acute spinal transection during administration of agonists for 5-HT1B/1D and NMDA receptors.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Oct 1;116(4):1644-1653. doi: 10.1152/jn.00198.2016. Epub 2016 Jul 13. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27486104 Free PMC article.
-
Fictive Scratching Patterns in Brain Cortex-Ablated, Midcollicular Decerebrate, and Spinal Cats.Front Neural Circuits. 2020 Feb 27;14:1. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2020.00001. eCollection 2020. Front Neural Circuits. 2020. PMID: 32174815 Free PMC article.
-
Motoneuron intrinsic properties, but not their receptive fields, recover in chronic spinal injury.J Neurosci. 2013 Nov 27;33(48):18806-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2609-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24285887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abhold RH, Bowker RM (1990) Descending modulation of dorsal horn biogenic amines as determined by in vivo dialysis. Neurosci Lett 108: 231-236. - PubMed
-
- Alstermark B, Kummel H, Tantisira B (1987) Monosynaptic raphespinal and reticulospinal projection to forelimb motoneurones in cats. Neurosci Lett 74: 286-290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
