Anti-CD11d integrin antibody treatment restores normal serotonergic projections to the dorsal, intermediate, and ventral horns of the injured spinal cord
- PMID: 15659600
- PMCID: PMC6725335
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3960-04.2005
Anti-CD11d integrin antibody treatment restores normal serotonergic projections to the dorsal, intermediate, and ventral horns of the injured spinal cord
Abstract
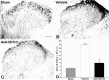
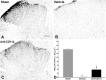
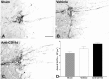
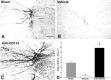
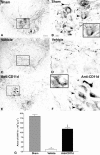
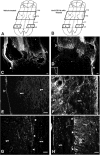
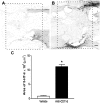
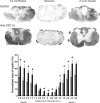
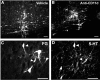
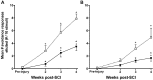
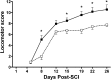
Spinal serotonergic pathways provide inhibitory and excitatory modulation of sensory, autonomic, and motor processing. After spinal cord injury (SCI), the acute inflammatory response is one process that damages descending pathways. Increases in serotonergic fiber density in spinal segments rostral and decreases caudal to the lesion have been observed previously and may contribute to neuropathic pain and motor dysfunction associated with SCI. We investigated the effect of an acute anti-inflammatory treatment on the density of serotonergic fibers rostral and caudal to a thoracic SCI lesion. This treatment, a monoclonal antibody to the CD11d subunit of the leukocyte CD11d/CD18 integrin, limits the trafficking of neutrophils and macrophages into the SCI site. In the dorsal horn, after treatment, the typically increased serotonin immunoreactivity rostral to injury was reduced, whereas that caudal to the lesion increased toward normal. Coincidently, mechanical allodynia in the dorsal trunk and hindpaws was significantly reduced. Increased serotonergic fiber density below the lesion also occurred in the intermediolateral cell column and ventral horn of treated rats, relative to controls. Improved locomotor recovery paralleled this increased serotonin. The treatment increased compact myelin in and near the lesion epicenter and increased serotonergic fiber bundles coursing around part of the lesion but had no consistent effect on the number of raphe-spinal neurons retrogradely labeled by tracer injection below the injury. In conclusion, this anti-CD11d integrin antibody treatment is neuroprotective after SCI, corresponding with improved patterns of intraspinal serotonergic innervation. The improvement in serotonergic fiber projections paralleled reduced mechanical allodynia and enhanced locomotor recovery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transient blockade of the CD11d/CD18 integrin reduces secondary damage after spinal cord injury, improving sensory, autonomic, and motor function.J Neurosci. 2004 Apr 21;24(16):4043-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5343-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15102919 Free PMC article.
-
Timing and duration of anti-alpha4beta1 integrin treatment after spinal cord injury: effect on therapeutic efficacy.J Neurosurg Spine. 2009 Nov;11(5):575-87. doi: 10.3171/2009.6.SPINE08915. J Neurosurg Spine. 2009. PMID: 19929361
-
Alpha4beta1 integrin blockade after spinal cord injury decreases damage and improves neurological function.Exp Neurol. 2008 Dec;214(2):147-59. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.04.024. Epub 2008 May 1. Exp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 19038604
-
The role of the serotonergic system in locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury.Front Neural Circuits. 2015 Feb 9;8:151. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00151. eCollection 2014. Front Neural Circuits. 2015. PMID: 25709569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transplants and neurotrophic factors increase regeneration and recovery of function after spinal cord injury.Prog Brain Res. 2002;137:257-73. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(02)37020-1. Prog Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12440372 Review.
Cited by
-
An overview of pharmacological approaches for management and repair of spinal cord injuries.Iran J Psychiatry. 2010 Fall;5(4):119-27. Iran J Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 22952505 Free PMC article.
-
Conditioned medium from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves recovery after spinal cord injury in rats: an original strategy to avoid cell transplantation.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 27;8(8):e69515. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069515. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24013448 Free PMC article.
-
CD11d integrin blockade reduces the systemic inflammatory response syndrome after traumatic brain injury in rats.Exp Neurol. 2015 Sep;271:409-22. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Jul 11. Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26169930 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of non-invasive pharmacologic neuroprotective treatments for acute spinal cord injury.J Neurotrauma. 2011 Aug;28(8):1545-88. doi: 10.1089/neu.2009.1149. Epub 2010 Apr 14. J Neurotrauma. 2011. PMID: 20146558 Free PMC article.
-
p53 Regulates the neuronal intrinsic and extrinsic responses affecting the recovery of motor function following spinal cord injury.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 3;32(40):13956-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1925-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23035104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ainge G, Cook JL, Gisby PT (1969) Rapid staining of myelin in paraffin sections with Luxol fast blue MBS. J Med Lab Technol 26: 231-232. - PubMed
-
- Ali Z, Wu G, Kozlov A, Barasi S (1996) The role of 5HT3 in nociceptive processing in the rat spinal cord: results from behavioural and electrophysiological studies. Neurosci Lett 208: 203-207. - PubMed
-
- Allen GV, Cechetto DF (1994) Serotoninergic and nonserotoninergic neurons in the medullary raphe system have axon collateral projections to autonomic and somatic cell groups in the medulla and spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 350: 357-366. - PubMed
-
- Bao F, Chen Y, Dekaban GA, Weaver LC (2004a) An anti-CD11d integrin antibody reduces cyclooxygenase-2 expression and protein and DNA oxidation after spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurochem 90: 1194-1204. - PubMed
-
- Bao F, Chen Y, Dekaban GA, Weaver LC (2004b) Early anti-inflammatory treatment reduces lipid peroxidation and protein nitration after spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurochem 88: 1335-1344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
