Mystique is a new insulin-like growth factor-I-regulated PDZ-LIM domain protein that promotes cell attachment and migration and suppresses Anchorage-independent growth
- PMID: 15659642
- PMCID: PMC1073663
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1052
Mystique is a new insulin-like growth factor-I-regulated PDZ-LIM domain protein that promotes cell attachment and migration and suppresses Anchorage-independent growth
Abstract
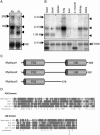
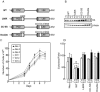
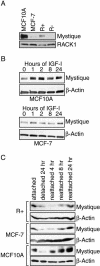
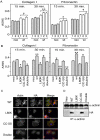
By comparing differential gene expression in the insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-IR null cell fibroblast cell line (R- cells) with cells overexpressing the IGF-IR (R+ cells), we identified the Mystique gene expressed as alternatively spliced variants. The human homologue of Mystique is located on chromosome 8p21.2 and encodes a PDZ LIM domain protein (PDLIM2). GFP-Mystique was colocalized at cytoskeleton focal contacts with alpha-actinin and beta1-integrin. Only one isoform of endogenous human Mystique protein, Mystique 2, was detected in cell lines. Mystique 2 was more abundant in nontransformed MCF10A breast epithelial cells than in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells and was induced by IGF-I and cell adhesion. Overexpression of Mystique 2 in MCF-7 cells suppressed colony formation in soft agarose and enhanced cell adhesion to collagen and fibronectin. Point mutation of either the PDZ or LIM domain was sufficient to reverse suppression of colony formation, but mutation of the PDZ domain alone was sufficient to abolish enhanced adhesion. Knockdown of Mystique 2 with small interfering RNA abrogated both adhesion and migration in MCF10A and MCF-7 cells. The data indicate that Mystique is an IGF-IR-regulated adapter protein located at the actin cytoskeleton that is necessary for the migratory capacity of epithelial cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Actopaxin, a new focal adhesion protein that binds paxillin LD motifs and actin and regulates cell adhesion.J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1435-48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.7.1435. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11134073 Free PMC article.
-
The activated insulin-like growth factor I receptor induces depolarization in breast epithelial cells characterized by actin filament disassembly and tyrosine dephosphorylation of FAK, Cas, and paxillin.Exp Cell Res. 1999 Aug 25;251(1):244-55. doi: 10.1006/excr.1999.4566. Exp Cell Res. 1999. PMID: 10438590
-
Essential function for PDLIM2 in cell polarization in three-dimensional cultures by feedback regulation of the β1-integrin-RhoA signaling axis.Neoplasia. 2014 May;16(5):422-31. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.04.006. Epub 2014 May 23. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 24863845 Free PMC article.
-
[PDLIM2 and Its Role in Oncogenesis--Tumor Suppressor or Oncoprote?].Klin Onkol. 2015;28 Suppl 2:2S40-6. doi: 10.14735/amko20152s40. Klin Onkol. 2015. PMID: 26374157 Review. Czech.
-
PDZ and LIM domain-encoding genes: molecular interactions and their role in development.ScientificWorldJournal. 2007 Sep 1;7:1470-92. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2007.232. ScientificWorldJournal. 2007. PMID: 17767364 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PDLIM7 Synergizes With PDLIM2 and p62/Sqstm1 to Inhibit Inflammatory Signaling by Promoting Degradation of the p65 Subunit of NF-κB.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 4;11:1559. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01559. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849529 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the interaction between Actinin-Associated LIM Protein (ALP) and the rod domain of alpha-actinin.BMC Cell Biol. 2009 Mar 27;10:22. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-10-22. BMC Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19327143 Free PMC article.
-
PDlim2 selectively interacts with the PDZ binding motif of highly pathogenic avian H5N1 influenza A virus NS1.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e19511. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019511. Epub 2011 May 23. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21625420 Free PMC article.
-
PDLIM2 Suppression Inhibit Proliferation and Metastasis in Kidney Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 15;13(12):2991. doi: 10.3390/cancers13122991. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34203785 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleocytoplasmic functions of the PDZ-LIM protein family: new insights into organ development.Bioessays. 2010 Feb;32(2):100-8. doi: 10.1002/bies.200900148. Bioessays. 2010. PMID: 20091751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bach, I. (2000). The LIM domain: regulation by association. Mech. Dev. 91, 5–17. - PubMed
-
- Baserga, R., Peruzzi, F., and Reiss, K. (2003). The IGF-1 receptor in cancer biology. Int. J. Cancer 107, 873–877. - PubMed
-
- Bashirova, A. A., Markelov, M. L., Shlykova, T. V., Levshenkova, E. V., Alibaeva, R. A., and Frolova, E. I. (1998). The human RIL gene: mapping to human chromosome 5q31.1, genomic organization and alternative transcripts. Gene 210, 239–245. - PubMed
-
- Boden, S. D., Liu, Y., Hair, G. A., Helms, J. A., Hu, D., Racine, M., Nanes, M. S., and Titus, L. (1998). LMP-1, a LIM-domain protein, mediates BMP-6 effects on bone formation. Endocrinology 139, 5125–5134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

