Characterization of a truncated lipoarabinomannan from the Actinomycete Turicella otitidis
- PMID: 15659663
- PMCID: PMC545729
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.3.854-861.2005
Characterization of a truncated lipoarabinomannan from the Actinomycete Turicella otitidis
Abstract
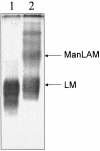
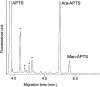
Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) lipoglycans have been characterized from a range of mycolic acid-containing actinomycetes and from the amycolate actinomycete Amycolatopsis sulphurea. To further understand the structural diversity of this family, we have characterized the lipoglycan of the otic commensal Turicella otitidis. T. otitidis LAM (TotLAM) has been determined to consist of a mannosyl phosphatidylinositol anchor unit carrying an (alpha 1-->6)-linked mannan core and substituted with terminal-arabinosyl branches. Thus, TotLAM has a novel truncated LAM structure. Using the human monocytic THP-1 cell line, it was found that TotLAM exhibited only minimal ability to induce tumor necrosis factor alpha. These findings contribute further to our understanding of actinomycete LAM diversity and allow further speculation as to the correlation between LAM structure and the immunomodulatory activities of these lipoglycans.
Figures
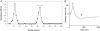
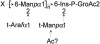

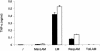
Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel mannose-capped lipoarabinomannan from Amycolatopsis sulphurea.Biochem J. 2003 Jun 15;372(Pt 3):821-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030197. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12620092 Free PMC article.
-
A single arabinan chain is attached to the phosphatidylinositol mannosyl core of the major immunomodulatory mycobacterial cell envelope glycoconjugate, lipoarabinomannan.J Biol Chem. 2014 Oct 31;289(44):30249-30256. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.599415. Epub 2014 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25231986 Free PMC article.
-
Tsukamurella paurometabola lipoglycan, a new lipoarabinomannan variant with pro-inflammatory activity.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 28;279(22):22973-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M310906200. Epub 2004 Mar 18. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15031299
-
Metabolism and gene sequence variation in Turicella otitidis implies its adaptability and pathogenicity in extra-otic infection: a systematic review.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Oct 27;23(1):735. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08721-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37891485 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoarabinomannans: from structure to biosynthesis.Biochimie. 2003 Jan-Feb;85(1-2):153-66. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(03)00048-8. Biochimie. 2003. PMID: 12765785 Review.
Cited by
-
Manipulation of the endocytic pathway and phagocyte functions by Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Jan 12;4:187. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00187. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25629008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macroamphiphilic components of thermophilic actinomycetes: identification of lipoteichoic acid in Thermobifida fusca.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jan;191(1):152-60. doi: 10.1128/JB.01105-08. Epub 2008 Oct 17. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 18931132 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoteichoic acid in Streptomyces hygroscopicus: structural model and immunomodulatory activities.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e26316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026316. Epub 2011 Oct 18. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22028855 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoarabinomannan in sputum to detect bacterial load and treatment response in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis: Analytic validation and evaluation in two cohorts.PLoS Med. 2019 Apr 12;16(4):e1002780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002780. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Med. 2019. PMID: 30978194 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the molecular basis of mycobacteria and lipoglycan recognition by the C-type lectin Dectin-2.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 15;8(1):16840. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35393-5. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30443026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Assaf, N. A., and W. A. Dick. 1993. Spheroplast formation and plasmid isolation from Rhodococcus spp. BioTechniques 15:1010-1012, 1014-1015. - PubMed
-
- Bax, A., and D. G. Davis. 1985. MLEV-17-based two-dimensional homonuclear magnetization transfer spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 65:355-360.
-
- Bax, A., and S. Subramanian. 1986. Sensitivity-enhanced two-dimensional heteronuclear shift correlation NMR spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 67:565-569.
-
- Bax, A., and M. F. Summers. 1986. H-1 and C-13 assignments from sensitivity enhanced detection of heteronuclear multiple bound connectivity by 2D multiple quantum NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 108:2093-2094.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

