Characterization of the pheromone response of the Enterococcus faecalis conjugative plasmid pCF10: complete sequence and comparative analysis of the transcriptional and phenotypic responses of pCF10-containing cells to pheromone induction
- PMID: 15659682
- PMCID: PMC545727
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.3.1044-1054.2005
Characterization of the pheromone response of the Enterococcus faecalis conjugative plasmid pCF10: complete sequence and comparative analysis of the transcriptional and phenotypic responses of pCF10-containing cells to pheromone induction
Abstract
The sex pheromone plasmids in Enterococcus faecalis are one of the most efficient conjugative plasmid transfer systems known in bacteria. Plasmid transfer rates can reach or exceed 10(-1) transconjugants per donor in vivo and under laboratory conditions. We report the completion of the DNA sequence of plasmid pCF10 and the analysis of the transcription profile of plasmid genes, relative to conjugative transfer ability following pheromone induction. These experiments employed a mini-microarray containing all 57 open reading frames of pCF10 and a set of selected chromosomal genes. A clear peak of transcription activity was observed 30 to 60 min after pheromone addition, with transcription subsiding 2 h after pheromone induction. The transcript activity correlated with the ability of donor cells to transfer pCF10 to recipient cells. Remarkably, aggregation substance (Asc10, encoded by the prgB gene) was present on the cell surface for a long period of time after pheromone-induced transcription of prgB and plasmid transfer ability had ceased. This observation could have relevance for the virulence of E. faecalis.
Figures

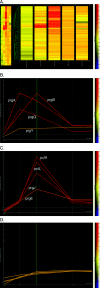

Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of the genes of Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pCF10 involved in replication and in negative control of pheromone-inducible conjugation.Plasmid. 1996 Jan;35(1):46-57. doi: 10.1006/plas.1996.0005. Plasmid. 1996. PMID: 8693026
-
Molecular and genetic analysis of a region of plasmid pCF10 containing positive control genes and structural genes encoding surface proteins involved in pheromone-inducible conjugation in Enterococcus faecalis.J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7650-64. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7650-7664.1991. J Bacteriol. 1991. PMID: 1938961 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of expression of prgX, a key negative regulator of the transfer of the Enterococcus faecalis pheromone-inducible plasmid pCF10.J Mol Biol. 2000 Apr 7;297(4):861-75. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3628. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10736223
-
The peptide pheromone-inducible conjugation system of Enterococcus faecalis plasmid pCF10: cell-cell signalling, gene transfer, complexity and evolution.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2007 Jul 29;362(1483):1185-93. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2007.2043. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17360276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide pheromone-induced transfer of plasmid pCF10 in Enterococcus faecalis: probing the genetic and molecular basis for specificity of the pheromone response.Peptides. 2001 Oct;22(10):1529-39. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(01)00489-2. Peptides. 2001. PMID: 11587782 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of virulence genes in Enterococcus species isolated from companion animals and livestock.Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 2018 Jun 27;85(1):e1-e8. doi: 10.4102/ojvr.v85i1.1583. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 30035595 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding bacterial type IV secretion lexicon.Res Microbiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;164(6):620-39. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2013.03.012. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Res Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23542405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissemination of Linezolid Resistance Through Sex Pheromone Plasmid Transfer in Enterococcus faecalis.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jun 4;11:1185. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01185. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32582110 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmids from Food Lactic Acid Bacteria: Diversity, Similarity, and New Developments.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jun 10;16(6):13172-202. doi: 10.3390/ijms160613172. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26068451 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enterococcus faecalis Sex Pheromone cCF10 Enhances Conjugative Plasmid Transfer In Vivo.mBio. 2018 Feb 13;9(1):e00037-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00037-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29440568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bae, T., S. Clerc-Bardin, and G. M. Dunny. 2000. Analysis of expression of prgX, a key negative regulator of the transfer of the Enterococcus faecalis pheromone-inducible plasmid pCF10. J. Mol. Biol. 297:861-875. - PubMed
-
- Bae, T., and G. M. Dunny. 2001. Dominant-negative mutants of prgX: evidence for a role for PrgX dimerization in negative regulation of pheromone-inducible conjugation. Mol. Microbiol. 39:1307-1320. - PubMed
-
- Bae, T., B. Kozlowicz, and G. M. Dunny. 2002. Two targets in pCF10 DNA for PrgX binding: their role in production of Qa and prgX mRNA and in regulation of pheromone-inducible conjugation. J. Mol. Biol. 315:995-1007. - PubMed
-
- Bae, T., B. K. Kozlowicz, and G. M. Dunny. 2004. Characterization of cis-acting prgQ mutants: evidence for two distinct repression mechanisms by Qa RNA and PrgX protein in pheromone-inducible enterococcal plasmid pCF10. Mol. Microbiol. 51:271-281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

