The DEAD box protein p68: a novel transcriptional coactivator of the p53 tumour suppressor
- PMID: 15660129
- PMCID: PMC548656
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600550
The DEAD box protein p68: a novel transcriptional coactivator of the p53 tumour suppressor
Abstract
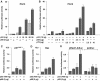
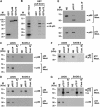
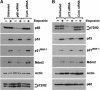
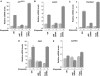
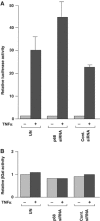
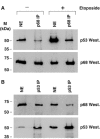
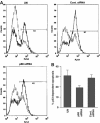
The DEAD box RNA helicase, p68, has been implicated in various cellular processes and has been shown to possess transcriptional coactivator function. Here, we show that p68 potently synergises with the p53 tumour suppressor protein to stimulate transcription from p53-dependent promoters and that endogenous p68 and p53 co-immunoprecipitate from nuclear extracts. Strikingly, RNAi suppression of p68 inhibits p53 target gene expression in response to DNA damage, as well as p53-dependent apoptosis, but does not influence p53 stabilisation or expression of non-p53-responsive genes. We also show, by chromatin immunoprecipitation, that p68 is recruited to the p21 promoter in a p53-dependent manner, consistent with a role in promoting transcriptional initiation. Interestingly, p68 knock-down does not significantly affect NF-kappaB activation, suggesting that the stimulation of p53 transcriptional activity is not due to a general transcription effect. This study represents the first report of the involvement of an RNA helicase in the p53 response, and highlights a novel mechanism by which p68 may act as a tumour cosuppressor in governing p53 transcriptional activity.
Figures


References
-
- Causevic M, Hislop RG, Kernohan NM, Carey FA, Kay RA, Steele RJ, Fuller-Pace FV (2001) Overexpression and poly-ubiquitylation of the DEAD-box RNA helicase p68 in colorectal tumours. Oncogene 20: 7734–7743 - PubMed
-
- Courtois S, Verhaegh G, North S, Luciani MG, Lassus P, Hibner U, Oren M, Hainaut P (2002) DeltaN-p53, a natural isoform of p53 lacking the first transactivation domain, counteracts growth suppression by wild-type p53. Oncogene 21: 6722–6728 - PubMed
-
- Deguin-Chambon V, Vacher M, Jullien M, May E, Bourdon JC (2000) Direct transactivation of c-Ha-Ras gene by p53: evidence for its involvement in p53 transactivation activity and p53-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene 19: 5831–5841 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

