The you gene encodes an EGF-CUB protein essential for Hedgehog signaling in zebrafish
- PMID: 15660164
- PMCID: PMC544551
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030066
The you gene encodes an EGF-CUB protein essential for Hedgehog signaling in zebrafish
Abstract
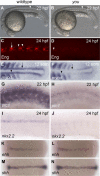
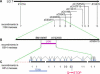
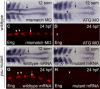
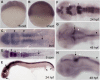
Hedgehog signaling is required for many aspects of development in vertebrates and invertebrates. Misregulation of the Hedgehog pathway causes developmental abnormalities and has been implicated in certain types of cancer. Large-scale genetic screens in zebrafish have identified a group of mutations, termed you-class mutations, that share common defects in somite shape and in most cases disrupt Hedgehog signaling. These mutant embryos exhibit U-shaped somites characteristic of defects in slow muscle development. In addition, Hedgehog pathway mutations disrupt spinal cord patterning. We report the positional cloning of you, one of the original you-class mutations, and show that it is required for Hedgehog signaling in the development of slow muscle and in the specification of ventral fates in the spinal cord. The you gene encodes a novel protein with conserved EGF and CUB domains and a secretory pathway signal sequence. Epistasis experiments support an extracellular role for You upstream of the Hedgehog response mechanism. Analysis of chimeras indicates that you mutant cells can appropriately respond to Hedgehog signaling in a wild-type environment. Additional chimera analysis indicates that wild-type you gene function is not required in axial Hedgehog-producing cells, suggesting that You is essential for transport or stability of Hedgehog signals in the extracellular environment. Our positional cloning and functional studies demonstrate that You is a novel extracellular component of the Hedgehog pathway in vertebrates.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Scube2 mediates Hedgehog signalling in the zebrafish embryo.Dev Biol. 2006 Jun 1;294(1):104-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.02.032. Epub 2006 Apr 13. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16626681
-
The zebrafish-secreted matrix protein you/scube2 is implicated in long-range regulation of hedgehog signaling.Curr Biol. 2005 Mar 8;15(5):480-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.02.018. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15753045
-
Two distinct cell populations in the floor plate of the zebrafish are induced by different pathways.Dev Biol. 2000 Mar 15;219(2):350-63. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1999.9589. Dev Biol. 2000. PMID: 10694427
-
Hedgehog signalling is required for maintenance of myf5 and myoD expression and timely terminal differentiation in zebrafish adaxial myogenesis.Dev Biol. 2001 Aug 1;236(1):136-50. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0193. Dev Biol. 2001. PMID: 11456450
-
Interactions between muscle fibers and segment boundaries in zebrafish.Dev Biol. 2005 Nov 15;287(2):346-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.08.049. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 16225858
Cited by
-
Distinct Cation Gradients Power Cholesterol Transport at Different Key Points in the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway.Dev Cell. 2020 Nov 9;55(3):314-327.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.08.002. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Dev Cell. 2020. PMID: 32860743 Free PMC article.
-
Scube2 expression extends beyond the central nervous system during mouse development.J Mol Histol. 2011 Oct;42(5):383-91. doi: 10.1007/s10735-011-9341-7. Epub 2011 Aug 6. J Mol Histol. 2011. PMID: 21822616
-
Perspectives on Intra- and Intercellular Trafficking of Hedgehog for Tissue Patterning.J Dev Biol. 2016 Dec 2;4(4):34. doi: 10.3390/jdb4040034. J Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 29615597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Inseparable Relationship Between Cholesterol and Hedgehog Signaling.Annu Rev Biochem. 2023 Jun 20;92:273-298. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-052521-040313. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Annu Rev Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37001135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overlapping roles and collective requirement for the coreceptors GAS1, CDO, and BOC in SHH pathway function.Dev Cell. 2011 Jun 14;20(6):775-87. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.04.018. Dev Cell. 2011. PMID: 21664576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McMahon AP, Ingham PW, Tabin CJ. Developmental roles and clinical significance of hedgehog signaling. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2003;53:1–114. - PubMed
-
- Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, Gailani MR, Shanley S, et al. Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell. 1996;85:841–851. - PubMed
-
- Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, Goodrich LV, Bare JW, et al. Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science. 1996;272:1668–1671. - PubMed
-
- Xie J, Murone M, Luoh SM, Ryan A, Gu Q, et al. Activating Smoothened mutations in sporadic basal-cell carcinoma. Nature. 1998;391:90–92. - PubMed
-
- Goodrich LV, Milenkovic L, Higgins KM, Scott MP. Altered neural cell fates and medulloblastoma in mouse patched mutants. Science. 1997;277:1109–1113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

