Desperate appliance
Figures
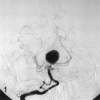
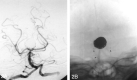
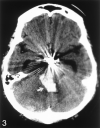
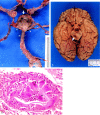


Comment on
-
A novel endovascular treatment of a wide-necked basilar apex aneurysm by using a Y-configuration, double-stent technique.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004 Mar;25(3):509-12. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004. PMID: 15037483 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Pipeline embolization of posterior communicating artery aneurysms associated with a fetal origin posterior cerebral artery.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017 Sep;160:83-87. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2017.06.014. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 28692909
-
Stent reconstruction of wide-necked aneurysms across the circle of Willis.Neurosurgery. 2007 Nov;61(5 Suppl 2):249-54; discussion 254-5. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000303977.04128.3e. Neurosurgery. 2007. PMID: 18091239 Clinical Trial.
-
Hemorrhagic complications related to the stent-remodeled coil embolization of intracranial aneurysms.Neurosurgery. 2010 Jul;67(1):73-8; discussion 78-9. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000370937.70207.95. Neurosurgery. 2010. PMID: 20559093
-
Intravascular stent and endovascular coil placement for a ruptured fusiform aneurysm of the basilar artery. Case report and review of the literature.J Neurosurg. 1997 Dec;87(6):944-9. doi: 10.3171/jns.1997.87.6.0944. J Neurosurg. 1997. PMID: 9384409 Review.
-
Stents for intracranial wide-necked aneurysms: more than mechanical protection.Neuroradiology. 2008 Dec;50(12):991-8. doi: 10.1007/s00234-008-0460-0. Epub 2008 Sep 20. Neuroradiology. 2008. PMID: 18807024 Review.
References
-
- Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Han P, McDougall CG. Preliminary experience using the Neuroform stent for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery 2004;54:6–16 - PubMed
-
- Shakespeare W. Hamlet. In: The tragedies of Shakespeare. New York: The Modern Library. 2:IV, iii, 9
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
