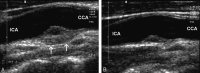
Ultrasonography of carotidynia
Figures
References
-
- Fay T. Atypical neuralgia. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 1927;18:309–315
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. Classification and diagnosis criteria for headache disorders, cranial neuralgias, and facial pain [Suppl]. Cephalgia 1988;8:48–49 - PubMed
-
- Upton PD, Smith JG, Charnock DR. Histologic confirmation of carotidynia. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2003;129:443–444 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
