The physiological regulation of toll-like receptor expression and function in humans
- PMID: 15661814
- PMCID: PMC1665604
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.081224
The physiological regulation of toll-like receptor expression and function in humans
Abstract
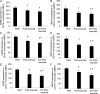
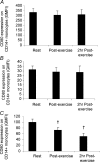
Eleven mammalian toll-like receptors (TLRs 1-11) have been identified to date and are known to play a crucial role in the regulation of immune responses; however, the factors that regulate TLR expression and function in vivo are poorly understood. Therefore, in the present study, we investigated the physiological regulation of TLR expression and function in humans. To examine the influence of diurnal rhythmicity on TLR expression and function, peripheral venous blood samples were collected from healthy volunteers (n = 8) at time points coinciding with the peak and nadir in the endogenous circulating cortisol concentration. While no diurnal rhythmicity in the expression of TLRs 1, 2, 4 or 9 was observed, the upregulation of costimulatory (CD80 and CD86) and antigen-presenting (MHC class II) molecules on CD14(+) monocytes following activation with specific TLR ligands was greater (P < 0.05) in samples obtained in the evening compared with the morning. To examine the influence of physical stress on TLR expression and function, peripheral venous blood samples were collected from healthy volunteers (n = 11) at rest and following 1.5 h of strenuous exercise in the heat (34 degrees C). Strenuous exercise resulted in a decrease (P < 0.005) in the expression of TLRs 1, 2 and 4 on CD14(+) monocytes. Furthermore, the upregulation of CD80, CD86, MHC class II and interleukin-6 by CD14(+) monocytes following activation with specific TLR ligands was decreased (P < 0.05) in samples obtained following exercise compared with at rest. These results demonstrate that TLR function is subject to modulation under physiological conditions in vivo and provide evidence for the role of immunomodulatory hormones in the regulation of TLR function.
Figures

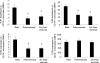
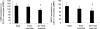
References
-
- Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 2001;413:732–738. 10.1038/35099560. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou L, Thomas V, Schnare M, Lobet Y, Anguita J, Schoen RT, Medzhitov R, Fikrig E, Flavell RA. Hyporesponsiveness to vaccination with Borrelia burgdorferi OspA in humans and in TLR1- and TLR2-deficient mice. Nat Med. 2002;8:878–884. - PubMed
-
- Aliprantis AO, Yang RB, Mark MR, Suggett S, Devaux B, Radolf JD, Klimpel GR, Godowski P, Zychlinsky A. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through toll-like receptor-2. Science. 1999;285:736–739. 10.1126/science.285.5428.736. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Almawi WY, Abou Jaoude MM, Li XC. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms of glucocorticoid antiproliferative effects. Hematol Oncol. 2002;20:17–32. 10.1002/hon.684. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Angeli A, Gatti G, Sartori ML, Masera RG. Chronobiological aspects of the neuroendocrine-immune network. Regulation of human natural killer (NK) cell activity as a model. Chronobiologia. 1992;19:93–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

