Carbon dioxide sensitivity during hypoglycaemia-induced, elevated metabolism in the anaesthetized rat
- PMID: 15661819
- PMCID: PMC1665607
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.080085
Carbon dioxide sensitivity during hypoglycaemia-induced, elevated metabolism in the anaesthetized rat
Abstract
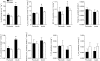
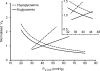
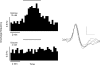
We have utilized an anaesthetized rat model of insulin-induced hypoglycaemia to test the hypothesis that peripheral chemoreceptor gain is augmented during hypermetabolism. Insulin infusion at 0.4 U kg (-1)min(-1) decreased blood glucose concentration significantly to 3.37 +/- 0.12 mmol l(-1). Whole-body metabolism and basal ventilation were elevated without increase in P(a,CO(2)) (altered non-significantly from the control level, to 37.3 +/- 2.6 mmHg). Chemoreceptor gain, measured either as spontaneous ventilatory airflow sensitivity to P(a,CO(2)) during rebreathing, or by phrenic minute activity responses to altered P(a,CO(2)) induced by varying the level of artificial ventilation, was doubled during the period of hypermetabolism. This stimulatory effect was primarily upon the mean inspiratory flow rate, or phrenic ramp component of breathing and was reduced by 75% following bilateral carotid sinus nerve section. In vitro recordings of single carotid body chemoafferents showed that reducing superfusate glucose concentration from 10 mM to 2 mM reduced CO(2) chemosensitivity significantly from 0.007 +/- 0.002 Hz mmHg(-1) to 0.001 +/- 0.002 Hz mmHg(-1). Taken together, these data suggest that the hyperpnoea observed during hypermetabolism might be mediated by an increase in the CO(2) sensitivity of the carotid body, and this effect is not due to the insulin-induced fall in blood glucose concentration.
Figures



References
-
- Asmussen E. Physiology of Muscular Exercise. New York: American Heart Association; 1967. Exercise and the regulation of ventilation; pp. 132–145.
-
- Asmussen E, Nielsen M. Studies on the regulation of respiration in heavy work. Acta Physiol Scand. 1946;12:171–178.
-
- Asmussen E, Nielsen M. Ventilatory response to CO2 during work at normal and at low oxygen tensions. Acta Physiol Scand. 1957;39:27–35. - PubMed
-
- Band DM, Linton RA. The effect of potassium and venous CO2 loading on chemoreceptor firing in anaesthetized cats. Respir Physiol. 1989;76:173–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

